FIG 1.
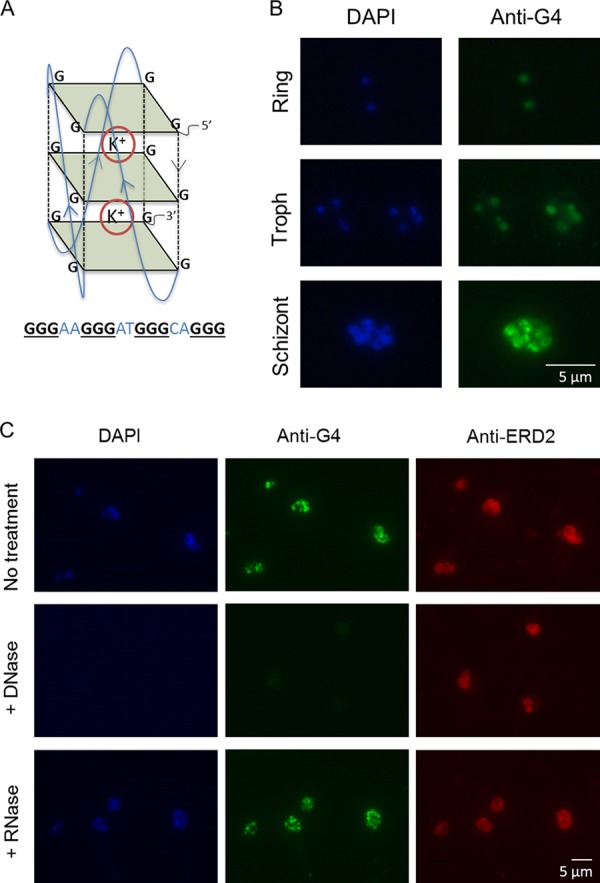
G-quadruplexes can be detected in P. falciparum parasites. (A) Schematic of a G-quadruplex DNA motif. Guanine tetrads are shown as green squares, and guanine backbones are shown as dashed black lines. G-quartets stack on top of one another to form the quadruplex, which is stabilized by cations, such as potassium (K+). An example of a PQS that could fold into such a structure is shown below. (B) Immunofluorescence images showing G-quadruplexes detected with the structure-specific antibody IH6 in P. falciparum intraerythrocytic stages (3D7 parasite strain). Images are representative of those from 3 independent experiments examining mixed-stage cultures. Troph, trophozoite. (C) DNase treatment abolishes G-quadruplex (IH6) staining but has no effect on the distribution of a protein, ERD2, used as a control (middle). RNase treatment has no discernible effect on G-quadruplex (IH6) staining (bottom). Images are representative of those from 3 independent experiments.
