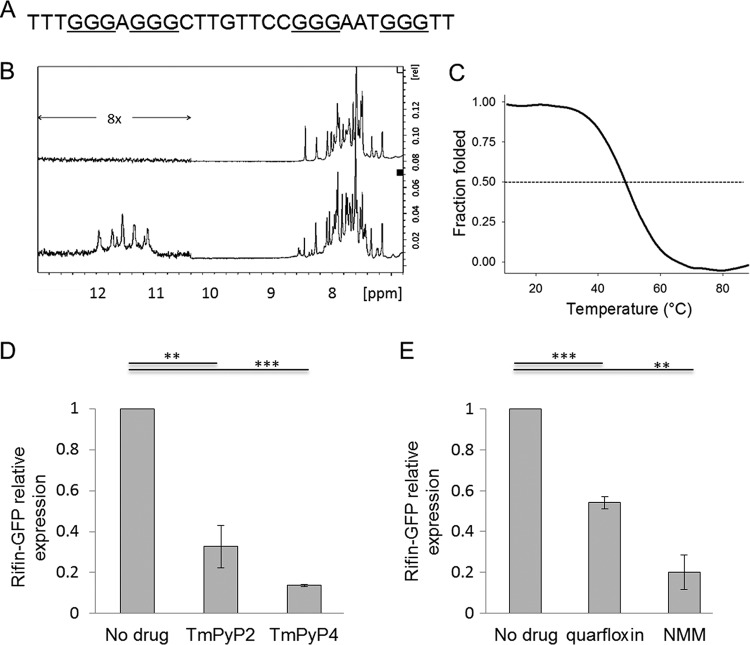
FIG 4.
G-quadruplex-binding drugs affect the expression of a G-quadruplex reporter gene. (A) Oligonucleotide sequence from the gene PF3D7_0700200, used in biophysical assays to confirm the folding of a G-quadruplex structure. (B) 1H NMR spectra, acquired at 37°C in 150 mM Li+ (top) and 150 mM K+ (bottom). Imino proton peaks are present only in K+, in agreement with the inability of Li+ to stabilize G-quadruplex structures. The relatively low intensity of imino peaks under the K+ condition seems to indicate the presence of a floppy structure, potentially the consequence of the second long loop. (C) Stability of the G-quadruplex as evaluated by thermal denaturation, followed at 295 nm. (D) Expression of the GFP-tagged G-quadruplex reporter gene PF3D7_0700200 in transgenic parasite cultures treated with 0.75 μM TMPyP4 or TMPyP2 for 6 h. Expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR using primer pair GFP_F/R and compared to the average expression of three housekeeping genes encoding actin, seryl-tRNA synthetase, and fructose bisphosphate aldolase. The experiment was carried out in both biological and technical duplicates, error bars are standard errors of the means, and statistical significance was assessed by a 1-tailed t test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (E) Expression of the GFP-tagged G-quadruplex reporter gene PF3D7_0700200 in transgenic parasite cultures treated with 120 nM quarfloxin or 80 μM NMM for 1 h, determined as described in the legend to panel D.