FIGURE 6.
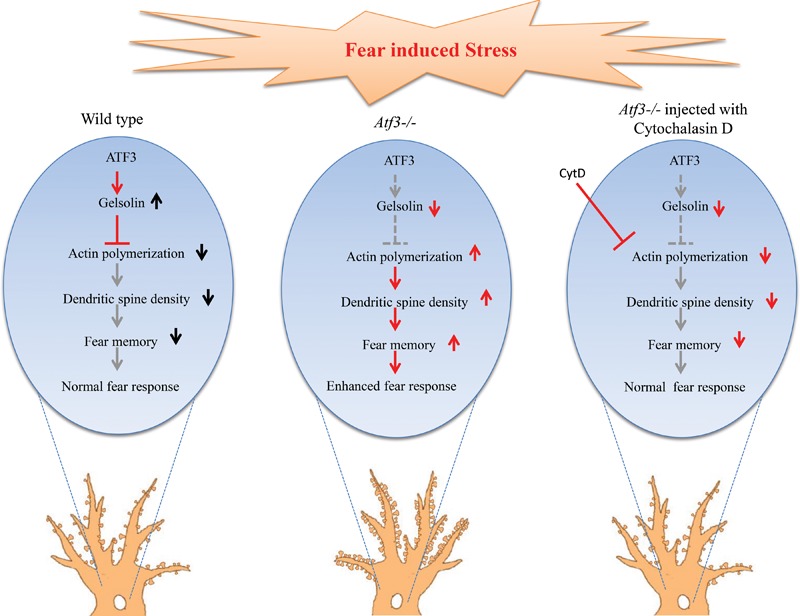
Hypothesized mechanism for ATF3 modulation of the fear response through actin polymerization and dendritic spine reorganization. Left: ATF3 modulates normal fear response by increasing the expression of Gelsolin, which is an actin polymerization inhibitor. The increase in Gelsolin results in decreased actin polymerization and thereby decreases dendritic spine density, resulting in normal fear memory formation. Centre: In the absence of ATF3, actin polymerization increases because of Gelsolin expression reduction, thereby resulting in increased spine density and higher fear response. Right: Injection of cytochalasin D, an inhibitor of actin polymerization, decreases dendritic spine density and reverses the higher freezing response of the Atf3-/- to the normal level.
