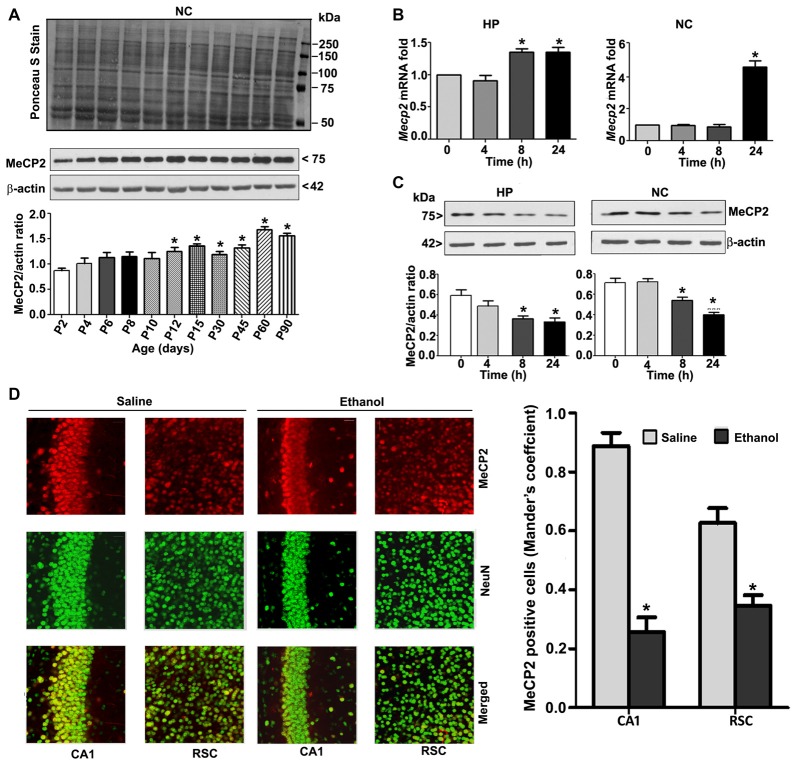
Figure 2.
MeCP2 protein expression pattern during mouse brain development; ethanol treatment of P7 mice enhances Mecp2 mRNA but impairs the protein levels in the HP and NC regions. (A) MeCP2 protein expression pattern during mouse brain development. The MeCP2 expression pattern in neocortical nuclear protein extract obtained from P2 to P90 mouse brains were subjected to western blotting. Equal protein loading was confirmed after Ponceau S staining, and β-actin was used as the protein loading control. (*p < 0.01 vs P2 groups; n = 12 pups/group). (B) RT-qPCR analysis of Mecp2 mRNA in HP and NC extracts obtained 4–24 h after the first saline or ethanol injection (n = 12 pups/group). Gapdh mRNA was used as the internal control for normalization of Mecp2 mRNA levels. (C) Western blot analysis of MeCP2 proteins in the P7 HP and NC nuclear protein extracts (4–24 h after the first saline or ethanol treatment). β-actin was used as the protein loading control. In the 0 h ethanol group, saline was injected [*p < 0.01 vs. saline (0 h) group]. (n = 12 pups/group). (D) The coronal brain sections (HP, hippocampus, and RSC, retrosplenial cortex; saline and 8 h ethanol) were used for immunohistochemistry with anti-mouse MeCP2 and anti-rabbit NeuN antibodies to label MeCP2-positive NeuN in neurons. Mander’s coefficient analysis was used to evaluate MeCP2-positive NeuN neurons in the CA1 and RSC brain regions. Error bars, SEM (*p < 0.01 vs. Saline, n = 6 pups/group). Scale bars = 10 μm. Error bars, SEM (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test).