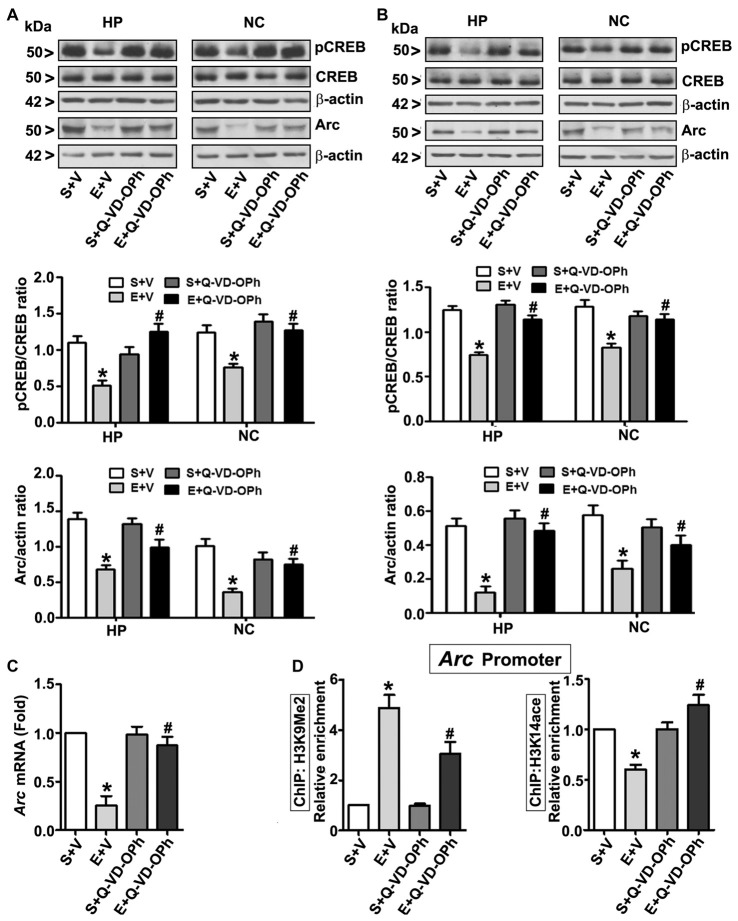
Figure 4.
Pharmacological blockades of caspase-3 activation protects against ethanol-induced inhibition of CREB phosphorylation and epigenetic-mediated activity regulatedcytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc) expression in the mouse brain. P7 pups were injected with Q-VD-OPh (1 mg/kg) 30 min before first saline or ethanol exposure and were either sacrificed after 8 h or were allowed to mature to adulthood and then sacrificed. (A) P7 and (B) adult hippocampal (HP) and neocortical (NC) nuclear extracts from the four treatment groups (S + V, E + V, S + Q-VD-OPh, or E + Q-VD-OPh) were subjected to western blotting to analyze the levels of pCREB, CREB and Arc (n = 10 pups/group). The representative blots are shown for the hippocampal and cortical nuclear extracts (*p < 0.01 vs. S + V; #p < 0.01 vs. E + V). β-actin was used as the loading control. (C) Adult hippocampal nuclear extracts from the four treatment groups (S + V, E + V, S + Q-VD-OPh, or E + Q-VD-OPh) were subjected to RT-qPCR to analyze the Arc mRNA levels. Hprt mRNA was used as the internal control for normalization of Arc mRNA. (D) Epigenetic analysis at the promoter region of the Arc gene. ChIP analysis of the Arc gene promoter in HP tissues from the four treatment groups (S + V, E + V, S + Q-VD-OPh, or E + Q-VD-OPh) with anti-acetylated H3K14 or anti-H3K9me2 antibodies. Levels of Arc gene promoter chromatin enrichment in the IPs were measured by RT-qPCR. Error bars, SEM (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test).