Figure 4.
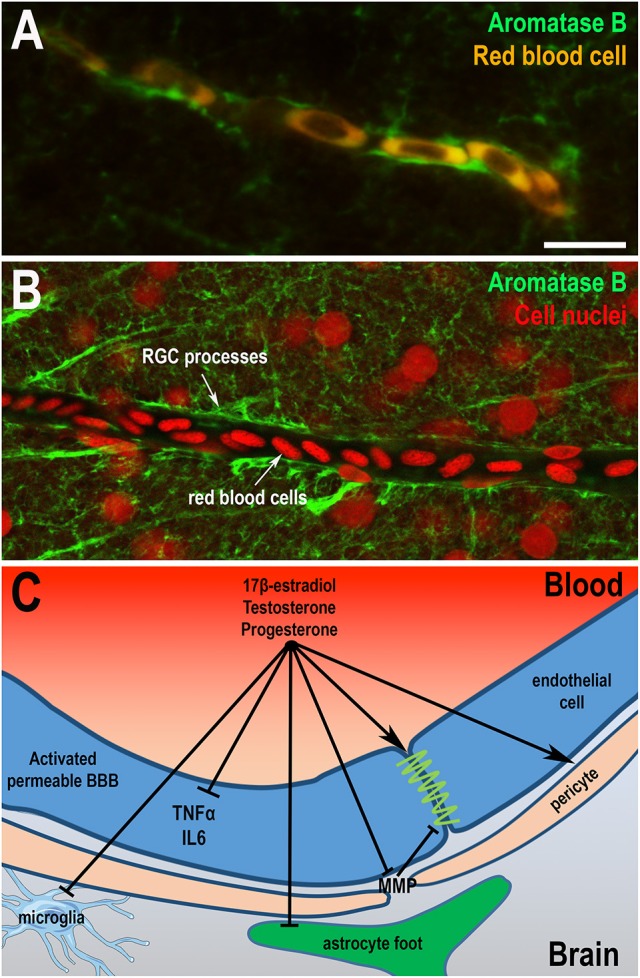
Sex hormones restore blood-brain barrier physiology and integrity. (A,B) Aromatase B immunohistochemistry (green) on zebrafish brain highlights that radial glial processes envelop blood vessels as shown by the auto-fluorescence of red blood cells (A) or by nuclear staining (B). These data suggest that radial glial cells could endorse the role of astrocytes in the establishment of the BBB, given the absence of astrocytic cell-type in the brain of fish. It also raises the question of the potential role of locally-produced estrogens on the BBB physiology. Scale bar: 7 μm. (C) Sex steroids (17β-E2, progesterone, and testosterone) display direct and indirect effects on the BBB through the restauration of thigh junctions, the inhibition of inflammatory cytokine expression and metalloproteinases production, the regulation of pericytes contraction, and consequently the modulation of cerebral blood flow. They also limit reactive gliosis through the inhibition of glial activation under pathological conditions (astrocytes and microglia). Sex steroids participate in the maintenance of a functional BBB, reducing neuroinflammation and promoting neuroprotection.
