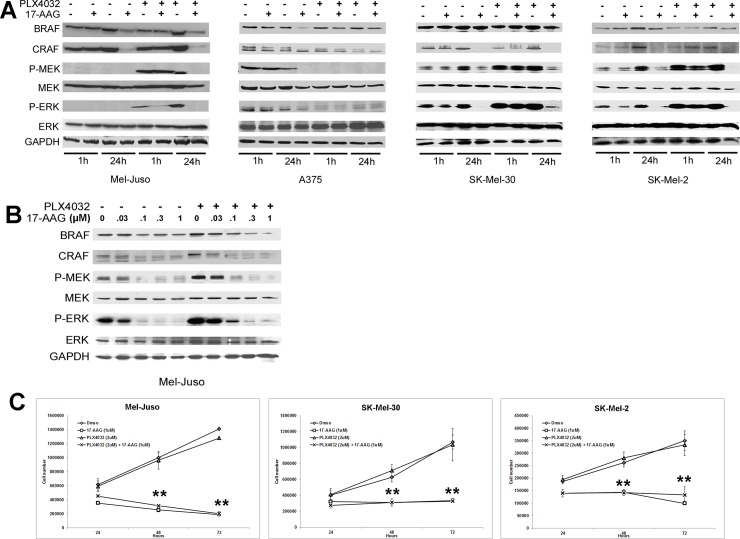
Fig 5. 17-AAG treatment inhibits PLX4032 enhanced MAPK signaling in BRAFWT human melanoma cells.
(A) Human melanoma cells (Mel-Juso, A375, SK-Mel-30 and SK-Mel-2) were pre-incubated with PLX4032 (2μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 24h and cells were further incubated with17-AAG (1μM) for 1h or 24h. Cell lysates were examined for the phosphorylation pattern of MAPK pathway by western blot. (B) Cultured human melanoma cell line Mel-Juso was pre-incubated with PLX4032 (2μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 24h and these cells were subsequently treated with increasing concentrations of 17-AAG (0, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3 or 1μM) for 24h. Cell lysates were collected and studied for phosphoprotein levels of MAPK pathway. (C) Human melanoma cell lines Mel-Juso, SK-Mel-30 and SK-Mel-2 were pre-incubated with PLX4032 (2μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 24h and were further treated with or without 17-AAG for 24, 48, and 72h. Time-dependent inhibition of human melanoma cell growth with PLX4032 and 17-AAG was determined by counting cells that exclude Trypan blue.