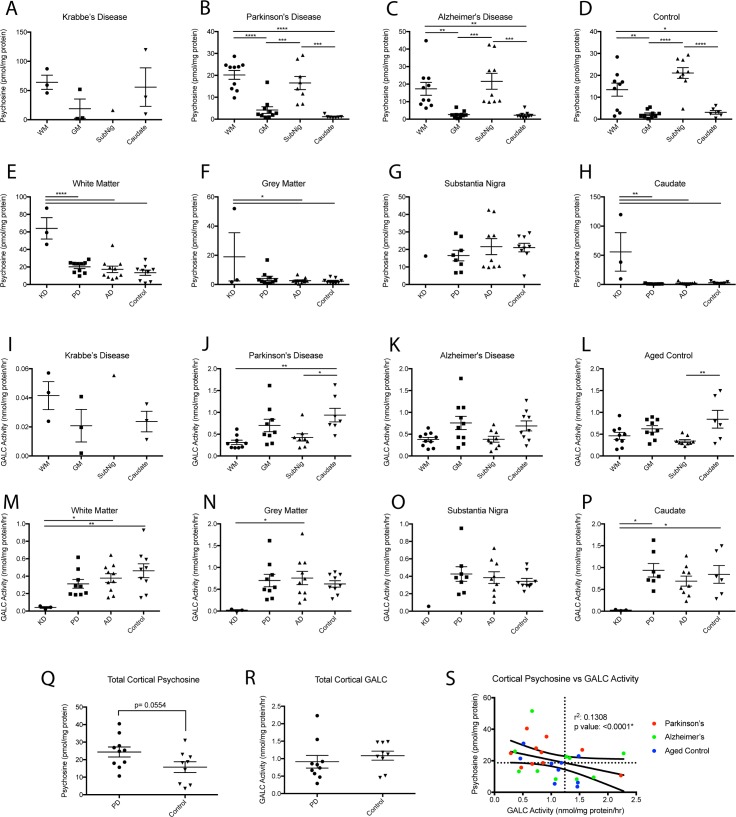
Fig 1. Psychosine content and GALC activity in neurodegenerative cohort.
Psychosine concentration in white (WM) and gray (GM) cortical matter, substantia nigra, and caudate was examined in patients diagnosed with Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Krabbe, or healthy controls. A-D) Psychosine was found to have a robust distribution, elevated in the white matter and substantia nigra of all patients. E-H) Psychosine in white and gray matter of Parkinson’s brains trended upwards compared to AD and healthy controls but did not reach significance. GALC activity in white (WM) and gray (GM) cortical matter, substantia nigra, and caudate was examined in patients diagnosed with Parkinsons’s, Alzheimer’s, Krabbe’s, or healthy controls. I-L) GALC activity was found to have a robust distribution, with lower levels found in the white matter and substantia nigra of all patients. M-P) GALC activity in white matter of Parkinson’s brains trended downwards compared to AD and healthy controls but did not reach significance. Q) Total cortical psychosine (summation of white and gray matter of cortex) found higher levels (p = 0.0554) of psychosine in Parkinson’s tissue compared to healthy controls. R) A total cortical GALC activity (summation of white and gray matter of cortex) did not find significantly different levels of GALC activity in Parkinson’s tissue compared to healthy controls. S) Correlation of psychosine to GALC activity as measured within the total cortical tissue of each group. (panel A-P: one way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, *p<0.05. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, panel Q,R: t-test).