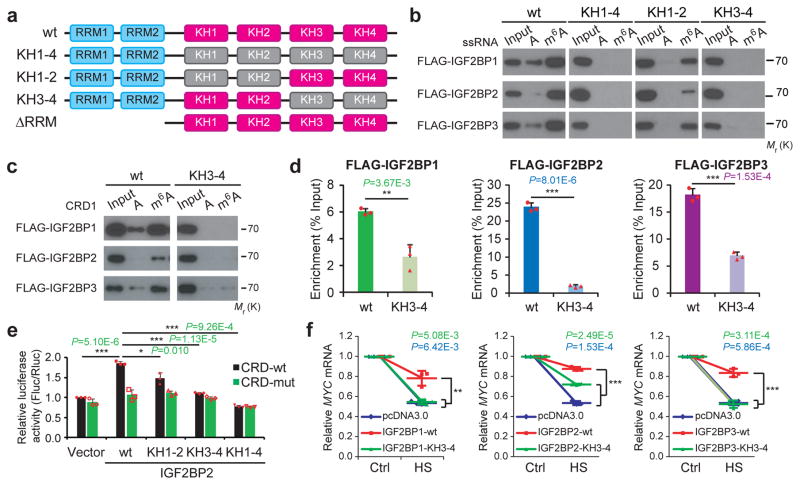
Figure 5. The KH domains of IGF2BPs are critical for m6A recognition and binding.
(a) Schematic structures showing RNA binding domains within IGF2BP proteins and a summary of IGF2BP variants used in this study. Blue boxes are RRM domains, red boxes are wild-type KH domains with GxxG core, and grey boxes are inactive KH domain with GxxG to GEEG conversions. (b) RNA pulldown followed by Western blotting showed in vitro binding of ssRNA baits with wild-type (wt) or KH domain-mutated IGF2BP variants, representative of 3 independent experiments. (c) In vitro binding of CRD1 RNA probes with wild-type or KH3-4 mutated IGF2BPs, representative of 3 independent experiments. (d) The association of wild-type and KH3-4 mutated IGF2BPs with MYC CRD in HEK293T cells as assessed by RIP-qPCR. (e) Relative luciferase activity of CRD reporters in HEK293T cells with forced expression of wild-type or mutated IGF2BP2 variants. (f) Changes in MYC mRNA levels in Hela cells with empty vector or forced expression of wild-type or KH3-4 mutated IGF2BPs one hour post-heat shock (HS). Values are mean±s.d. of n =3 independent experiments, and two-tailed Student’s t-tests were used in d, e, f (*, P <0.05; **, P <0.01; ***, P <0.001). Unprocessed scans of western blot analysis are available in Supplementary Figure 8. Source data of d, e, f are in Supplementary Table 3.