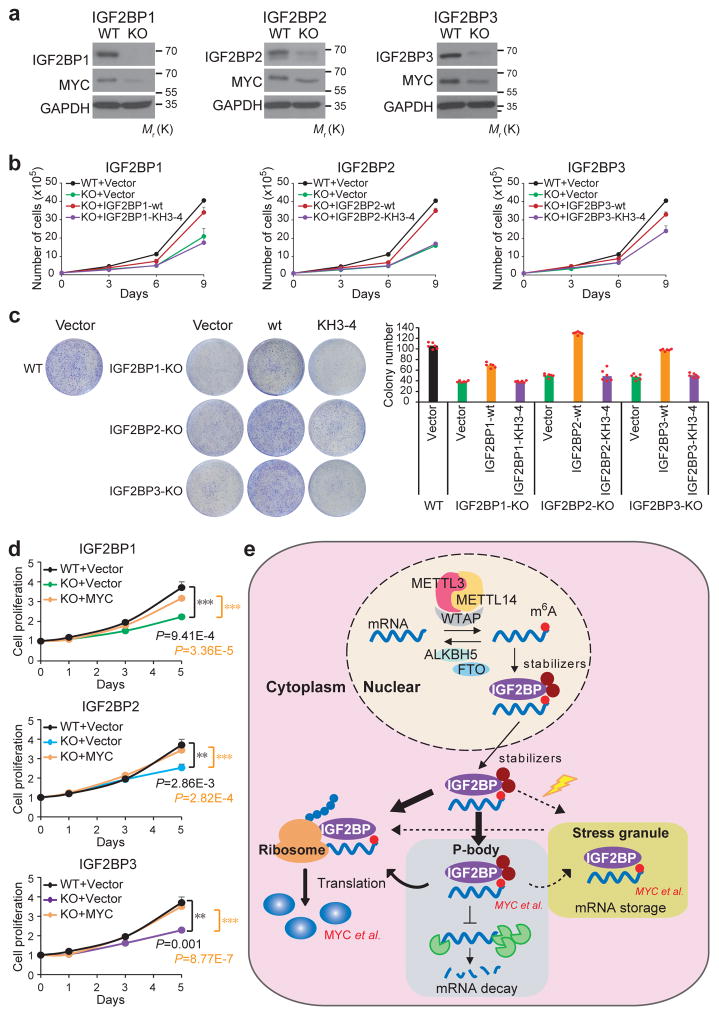
Figure 7. IGF2BPs are oncogenic m6A readers.
(a) CRISPR-Cas9 mediated knockout (KO) of IGF2BPs and the subsequent depletion of MYC in HepG2 cells as detected by Western blotting. Images were representative of 3 independent experiments. (b) Effect of wild-type or KH3-4 mutated IGF2BPs on restoring cell proliferation in IGF2BP-KO cells. Data shown represent mean value of viable cell numbers of 2 independent experiments. (c) Colony formation assay using wild-type (WT) or IGF2BP KO (sgIGF2BP) HepG2 cells. Representative images of crystal violet staining of cells were shown on top of the histograms of colony numbers. Colonies were counted from 3 replicate wells of and 2 independent experiments were performed. The colony number of each experiment represents the average count of 3 replicate wells. (d) MTT assays displaying the effect of MYC on restoring cell proliferation in IGF2BP-KO cells. Values are mean±s.d. of n =3 independent experiments. Two-tailed student t-test were used (**, P <0.01; ***, P <0.001). (e) Working model of IGF2BP-mediated regulation of m6A modified mRNAs. mRNAs were methylated de novo by the methyltransferase complex composed of METTL3, METTL14 and a regulatory subunit WTAP. The naïve mRNA with m6A modifications were preferentially recognized by IGF2BP proteins. By recruiting mRNA stabilizers, such as HuR and MATR3, IGF2BPs protect target mRNAs from degradation in the P-body while facilitating translation after being exported to cytoplasm. Under stress conditions such as heat shock, IGF2BP-containing mRNPs are translocated to stress granules for the storage of their mRNA targets. Unprocessed scans of western blot analysis are available in Supplementary Figure 8. Source data of b, c, d are in Supplementary Table 3.