Figure 5.
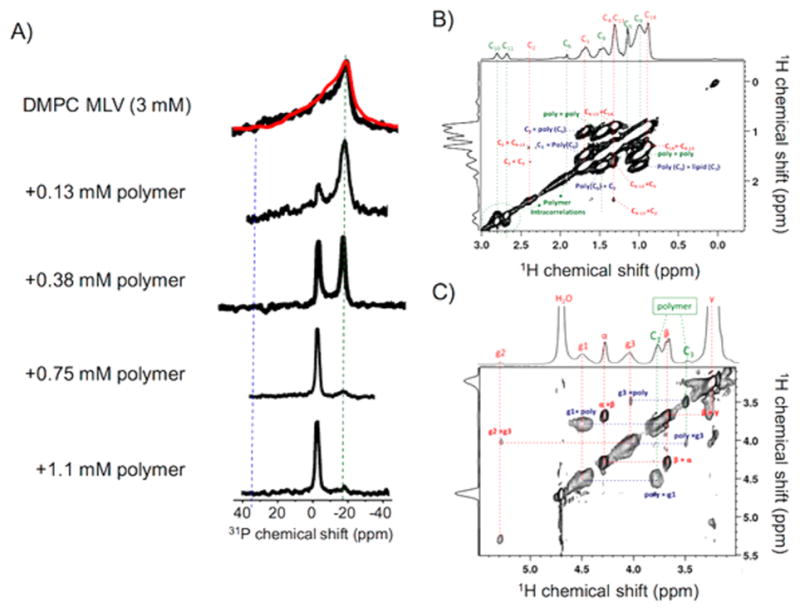
NMR experiments revealing the formation of nanodiscs. (A) 31P NMR spectra of 3 mM DMPC vesicles in the absence and presence of the indicated amount of polymer. The disappearance of the 31P chemical shift powder pattern and the increase in the intensity of a narrow isotropic peak (at −2.3 ppm) indicate the dissolution of MLVs and the formation of lipid bilayer nanodiscs. (B and C) 2D 1H–1H NOESY spectra of polymer nanodiscs containing DMPC lipids showing the interaction between the DMPC acyl chains and hydrophobic side chain of the methacrylate polymer, which provides evidence for the formation of an amphipathic belt by the polymers that surround the lipid bilayer; see the intermolecular contacts revealed by the cross peaks in the NOESY spectrum in Figure S4. A 2D 1H–1H NOESY spectrum of the lipid-free polymer solution is given in the Supporting Information (Figure S3).
