Figure 6.
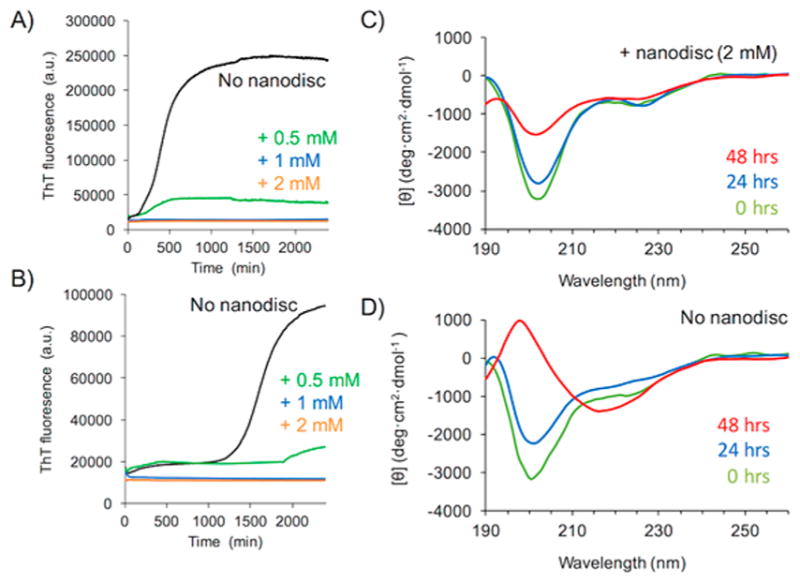
Polymer nanodiscs inhibit human-IAPP aggregation by stabilizing a helical intermediate. Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence experiments showing the aggregation of human-IAPP (at 20 μM (A) and 10 μM (B)) in the absence (black traces) and in the presence of polymer nanodiscs containing 0.5 mM (green), 1.0 mM (blue), and 2.0 mM (orange) of 9:1 DMPC:DMPG lipids. CD spectra of human-IAPP (at 20 μM) in the presence (C) and absence (D) of polymer nanodiscs containing 2.0 mM of 9:1 DMPC:DMPG lipids. ThT experiments reveal that the nanodiscs inhibit the aggregation of human-IAPP to form amyloid fibers, and the CD spectra show the formation of a helical intermediate of the peptide in 9:1 DMPC:DMPG lipid nanodiscs.
