Figure 1. S. Typhi Evades the Respiratory Burst in Neutrophil-like Cells Using the Vi Antigen.
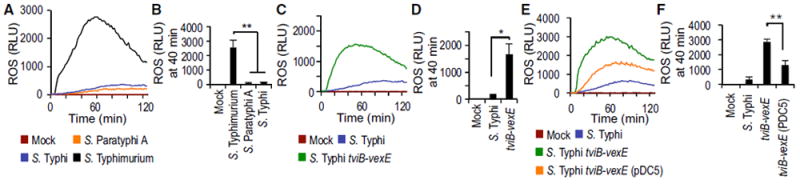
HL-60 cells were infected with the indicated opsonized bacterial strains and ROS production monitored over time using chemiluminescence.
(A and B) HL60 cells were infected with the indicated Salmonella serovars.
(C and D) HL60 cells were infected with capsulated and non-capsulated S. Typhi strains.
(E and F) HL60 cells were infected with S. Typhi wild type, a tviB-vexE mutant and a tviB-vexE mutant complemented by introducing the viaB locus on a plasmid (pDC5).
(A, C, and E) Representative experiment showing generation of chemiluminescence over time.
(B, D, and F) Quantification of chemiluminescence from three independent experiments at the indicated time point after infection. Bars represent means ± SE. Mock, mock infection; pDC5, XX; RLU, relative luminescence units. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
