Figure 7. Model for Evasion of the Phagocyte Respiratory Burst by Typhoidal Salmonella Serovars.
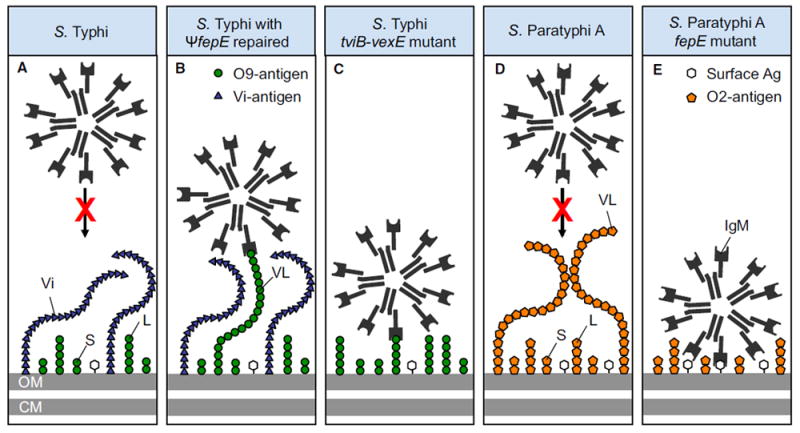
(A) The polysaccharide chains of the Vi antigen shield underlying surface structures from IgM binding.
(B) Restoration of the fepE pseudogene (ΨfepE) in S. Typhi results in production of very long O antigen chains that rival the Vi antigen in length, thereby elevating IgM binding to the bacterial surface.
(C) Deletion of the capsule biosynthesis genes in the S. Typhi tviB-vexE mutant exposes the short and long O antigen chains, thereby resulting in IgM binding.
(D) The very long O antigen chains of S. Paratyphi A contain the O2 antigen, which does not bind natural IgM, thereby shielding underlying surface structures.
(E) The short and long O antigen chains present in an S. Paratyphi A fepE mutant do not bind IgM, but are too short to prevent IgM binding to other surface antigens. Ag, antigens; CM, plasma membrane; L, long O antigen chains; OM, outer membrane; S, short O antigen chains; Vi, Vi antigen; VL, very long O antigen chains.
