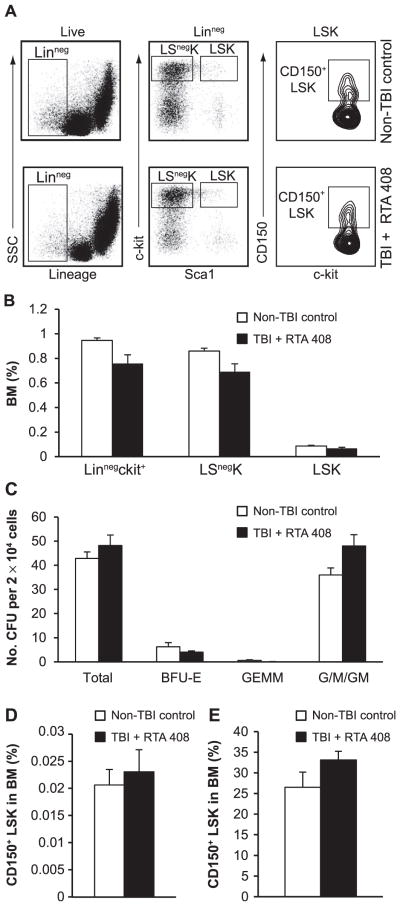
FIG. 3.
Restoration of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell frequency in RTA 408-mitigated 7.5 Gy TBI mice to non-TBI levels. Panel A: Representative flow cytometry analysis of 7.5 Gy TBI + RTA 408-treated mice and age-matched control BM, 14 weeks postirradiation. Parental populations are indicated on the top of each plot and gates used for analysis are shown. Panel B: Calculated frequency of hematopoietic progenitor populations based on flow cytometry analysis. No significant differences between control non-TBI mice (n = 5) and 7.5 Gy TBI + RTA 408-treated mice (n = 8) were observed. Panel C: Comparison of in vitro colony-forming unit activity in methylcellulose supplemented with IL3, IL6, TPO and SCF. There were no differences, in either the colonies per input BM or the types of colonies formed, between RTA 408-mitigated BM (n = 6) and age-matched non-TBI BM (n = 5). BFU-E: burst-forming-unit erythroid; GEMM: mixed lineage granulocytic, erythroid, macrophage, megakaryocyte; G/M/GM: myeloid colonies containing granulocytes (G), macrophages (M) or both cell types (GM). Panel D: CD150+LSK cell frequency in RTA 408-mitigated TBI mice (n = 8) is the same as in non-TBI, age-matched mice (n = 5). Panel E: Similar CD150+ cell frequency in the LSK compartments of RTA 408-mitigated BM and non-TBI BM. Unpaired Student’s t tests were used for statistical analysis. Error bars indicate SEM.