Table 1.
hPepT1 Homology Models
| Modela | Binding siteb | Volume (Å3)c |
Z- DOPEd |
PDB ID (Resolution)e |
Identityf | Organismg | Ligandh | Statei |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
141 | +0.12 | 2XUT (3.62 Å) | 34% | So | - | Occluded |
| 2 |

|
183 | −0.13 | 4APS (3.3 Å) | 22% | Sf | - | Unbound Inward-open |
| 3 |

|
291 | −0.18 | 4IKZ (2.4 Å) | 25% | Gk | Alafosfalin | Inward-open |
| 4 |
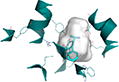
|
154 | −0.099 | 4D2C (2.47 Å) | 22% | St | Ala-Phe | Inward-open |
| 5 |
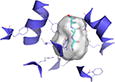
|
239 | −0.049 | 4D2D (2.52 Å) | 22% | St | Ala-Ala-Ala | Inward-open |
Model is the nomenclature used in this article.
Binding site shows surface representation of the binding site of the hPepT1 model calculated with POVME 2.0.51
Volume corresponds to the volume of the binding site calculated with the POVME 2.0.
Z-DOPE Score is the normalized atomic-distance dependent statistical potential based on known protein structures calculated by MODELLER.
PDB ID refers to the Protein Data Bank identifier of the template structure with the resolution of the structure in parentheses.
Identity is the percentage sequence identity between hPepT1 and the template structure calculated by HHPred.52
Organism refers to the organism of the template structure transporter: Shewanella oneidensis (So), Streptococcus thermophilus (St), Geobacillus kaustophilus (Gk).
Ligand corresponds to the small molecule bound to the binding site of the template structure.
Conformation refers to the conformation of the model.
