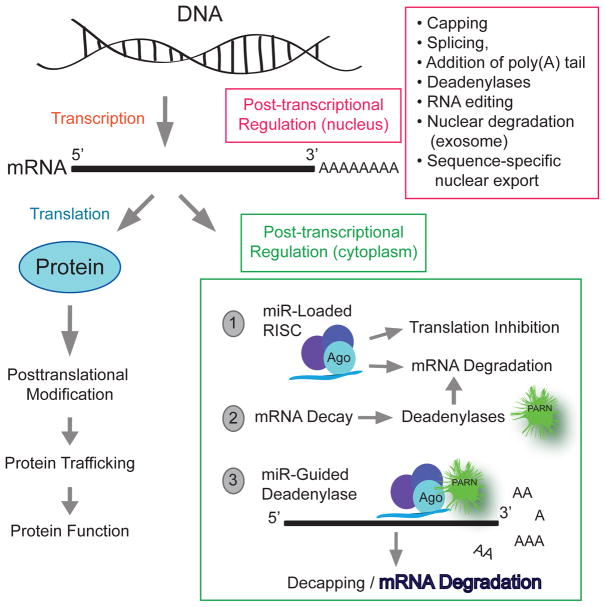
Figure 1. Post-transcriptional control of gene expression.
It comprises a complex regulatory network that contributes to cell-type and organism specific gene expression patterns. The pre-mRNA has to go through some modifications to become a mature mRNA molecule that can leave the nucleus and be translated. Those modifications include capping, splicing, addition of poly(A) tail, RNA editing, nuclear degradation (exosome), sequence-specific nuclear export mRNA, stability and lifetime in the cytosol and small regulatory RNAs, specifically microRNA (miRs). This review will focus on the three events (labeled “1”, “2” and “3”) occurring in the cytoplasm.