Figure 1.
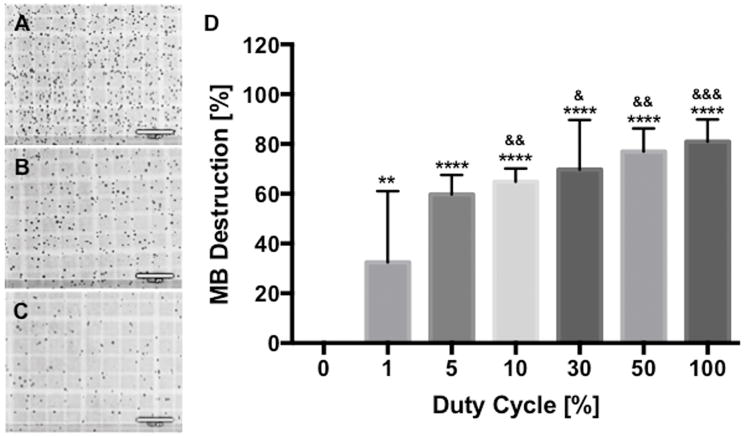
The higher duty cycle (DC) destroys the more microbubbles (MBs). MB suspension was exposed to DC-modulated ultrasound (US) and the number of MBs was counted using a hemocytometer. (A, B and C) Light microscopy shows that the greater number of MBs was destroyed by the sonication with the longer DC (0.27 W/cm2 for 10sec at 100% DC); (A) 0%, (B) 10% and (C) 100%. (D) Normalized percentage of remaining MBs after US exposure revealed that approximately 30% of MBs was destroyed at 1% DC and the percentage gradually increased when increasing DC. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n=4–10) and asterisks represent statistical significance compared with 0% DC and ampersands represent statistical significance compared with 1% DC (& p<0.05, ** and && p<0.01, &&& p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001). Bars = 100μm.