Figure 5.
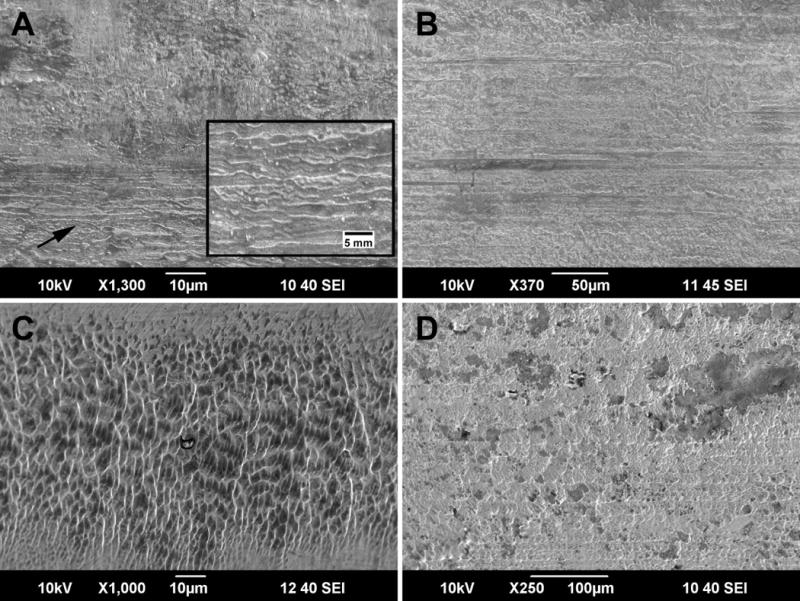
Fretting and fretting corrosion damage on CoCrMo alloy stem tapers (taper axis is vertical in all images) : A) Typical damage features of mechanically induced fretting wear. The lower half of the image shows fine ridges (arrow and higher magnification inset) that are usually located in areas of former machining marks and oriented perpendicular to the taper axis. B) SEM image of randomly oriented mechanically induced fretting marks after complete disruption of the initial machining mark topography. C) SEM image showing elongated pits, a typical damage feature of electrochemically-dominated fretting marks. D) Example of overlapping fretting damage features that were caused by mechanical and electrochemical fretting processes. For all images, the tapers are oriented proximal (top) to distal (bottom).
