Figure 9.
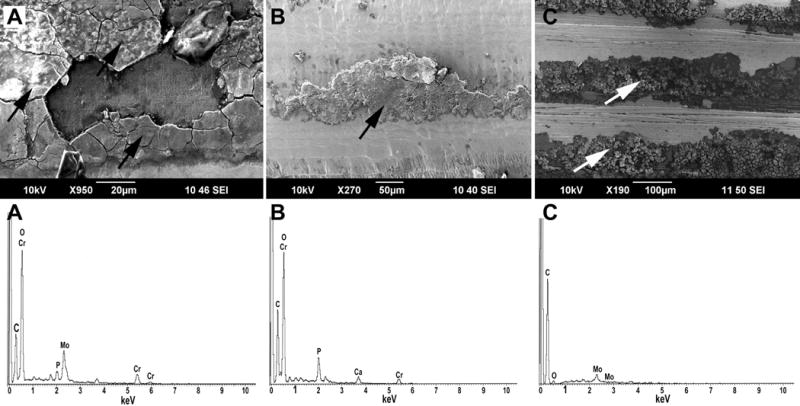
A) SEM image of thick deposit films covering an area of a CoCrMo stem taper that was affected by pitting corrosion. The EDS spectrum exhibited a prominent oxygen peak along with chromium and molybdenum, thus indicating that the deposits consisted mainly of mixed oxides. Cobalt was not present within the film. B) Another typical deposit (here on a CoCrMo head taper) that is usually located toward the distal end of the stem taper and around the opening of the head taper. The EDS spectrum revealed a prominent peak of phosphorus along with chromium and oxygen, thus confirming the presence of chromium phosphate. C) A Ti-alloy stem taper with another type of deposit, which was a carbonaceous- rich film that also exhibited a molybdenum peak, but no other metal. Often these deposits accumulated within the troughs of the stem taper topography. For all images, the tapers are oriented proximal (top) to distal (bottom).
