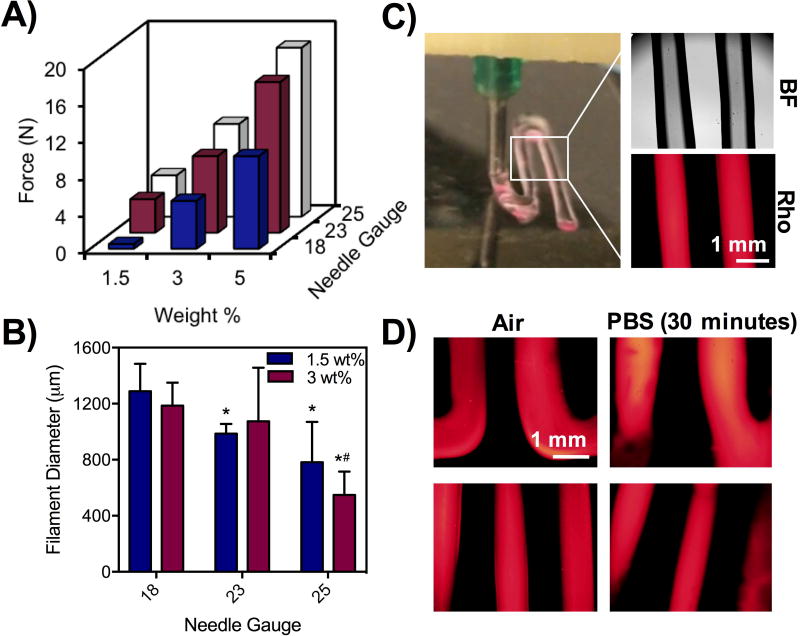
Figure 4. Effect of macromer concentration and needle gauge on force, filament printing, and viability.
A) Force measurements from Instron testing of hydrogels at 1.5, 3, and 5 wt% and 18, 23, and 25G needles at a rate of 2 mm/min. B) Quantification of filament diameters from 1.5 and 3 wt% hydrogels using 18, 23, and 25G needles. Hydrogels were encapsulated with rhodamine-dextran for imaging and quantification of filament size.*p<0.05 compared to 18G,#p<0.05 compared to 23G. C) Photo of printing with hydrogels containing rhodamine-dextran under bright field and fluorescent channels. D) Fluorescent images of filaments in air and in PBS after 30 minutes.