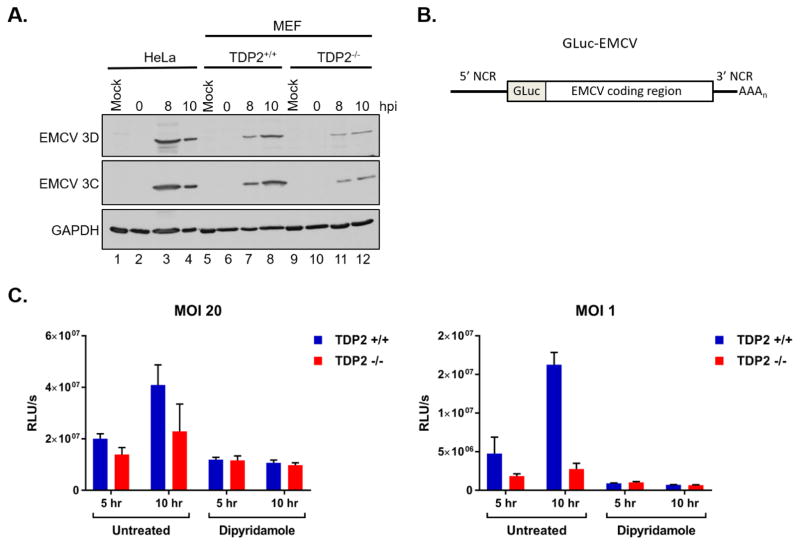
Fig. 3. EMCV viral protein accumulation is reduced in the absence of TDP2.
(A) HeLa, TDP2+/+ MEFs, and TDP2−/− MEFs were mock- or EMCV-infected at an MOI of 20. Cells and supernatant were collected at 0, 8, or 10 hr post-infection (hpi) and used to generate protein lysates. Lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using an anti-Mengo 3D, anti-EMCV 3C, or anti-GAPDH antibody to detect protein accumulation. (B) Schematic of the pdnGLuc-VFETQG-m16.1 construct used to generate the GLuc-EMCV virus. GLuc-EMCV encodes Gaussia luciferase immediately following the 5′ noncoding region (5′ NCR) and upstream of the complete EMCV coding region, 3′ NCR, and poly(A) tract. (C) TDP2+/+ and TDP2−/− MEFs were infected with GLuc-EMCV at an MOI of 1 or 20 and luciferase activity was measured at 5 and 10 hr post-infection. To inhibit viral RNA synthesis, cells were treated with 150 μM dipyridamole during and after virus adsorption. Luminescence is represented as relative light units per second (RLU/s) normalized to cell count. Data represent the means of triplicate experiments ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001 (Student’s t test)