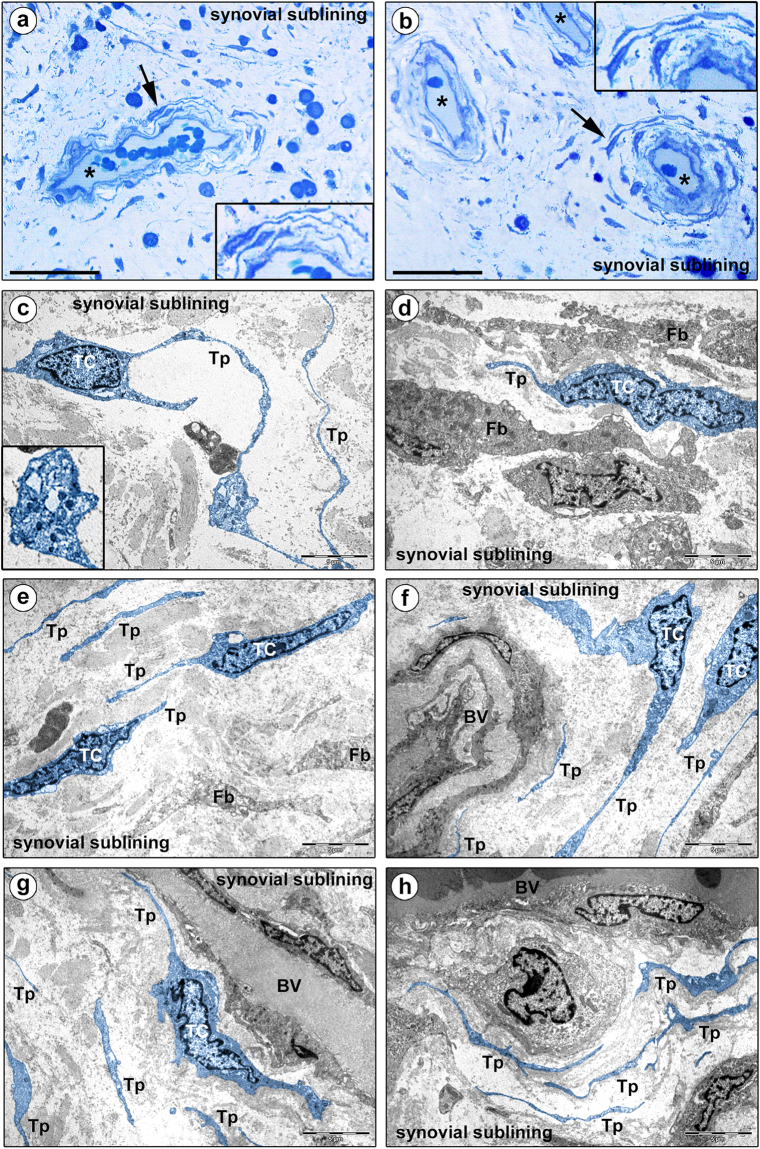
Figure 2.
Morphology of human synovium (sublining layer) under light and transmission electron microscopy. (a,b) Representative photomicrographs of toluidine blue-stained synovial semithin sections. Asterisks denote sublining layer blood vessels. Stromal cells displaying a spindle-shaped or piriform cell body with a large nucleus and very small amount of cytoplasm, and long and thin moniliform cytoplasmic processes are present throughout the synovial sublining, particularly in perivascular locations (arrows; shown at higher magnification in the insets). (c–h) Representative transmission electron microscopy photomicrographs of synovial ultrathin sections stained with uranyl acetate and bismuth subnitrate solutions. Telocytes (TC) and telopodes (Tp) have been digitally colored in blue. Telocytes are ultrastructurally characterized by i) a small cell body mostly occupied by a relatively large nucleus surrounded by scarce cytoplasm containing few mitochondria and cisternae of endoplasmic reticulum and a small Golgi apparatus, and ii) thin moniliform processes (telopodes) with narrow emergence from the cell body and a moniliform aspect (alternating thin segments/podomers and dilated portions/podoms). The nucleus is indented, showing patches of heterochromatin near the nuclear membrane. Podoms accommodate some organelles, such as rough endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria (c, inset). The ultrastructural traits of telocytes make them easily distinguishable from neighboring fibroblasts (Fb), which exhibit a large body rich in cisternae of rough endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria, a large Golgi apparatus and short and thick processes (d). Telocytes and telopodes can be observed throughout the whole synovial sublining layer, either in neutral positions surrounded by abundant collagenous extracellular matrix (c,e), or topographically closely related to fibroblasts (d) and blood vessels (BV) (f–h). Note the presence of telopodes delimiting the basal lamina of microvessels (f–h). Scale bar: 50 µm (a,b), 5 µm (c–h).