FIGURE 1.
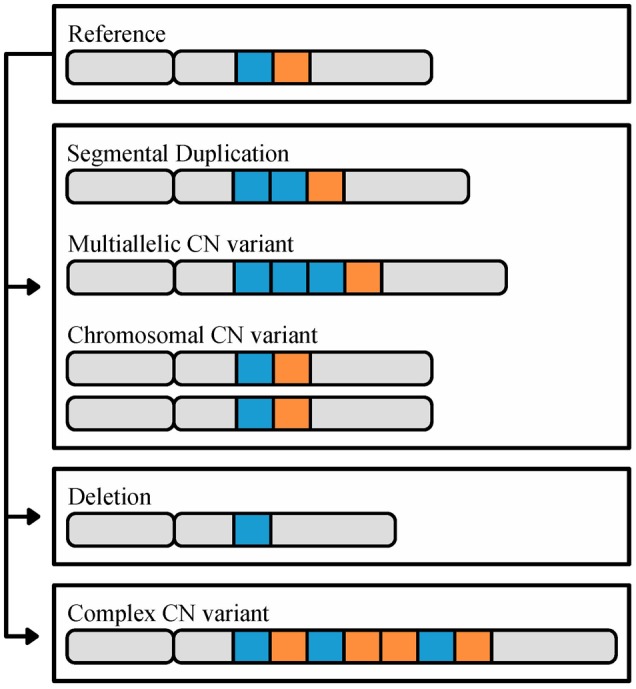
The different types of CN variation. CN variants range in size (50 base pairs or greater) to whole chromosomes, and are identified through comparison to a reference genome. In this cartoon, a reference chromosome containing two highlighted loci, in blue and orange, is shown on top. The second chromosome illustrates an example of a segmental duplication CN, in which there are two copies of the blue locus. The third chromosome illustrates an example of a multiallelic CN variant, where the duplicated locus contains 3 or more copies. The fourth pair of chromosomes illustrates a CN variant associated with the duplication of an entire chromosome. Finally, the last two chromosomes illustrate deletion and complex CN variants, respectively; deletion CN variants are associated with loci that are not present relative to the reference, and complex CN variants refer to a combination of duplications, deletions, insertions, and/or inversions relative to the reference. In some organisms, such as budding yeast (Dunn et al., 2012; Bergstrom et al., 2014) and humans (Riethman, 2009), CNVs tend to biased in their genomic location toward subtelomeres.
