Fig. 6.
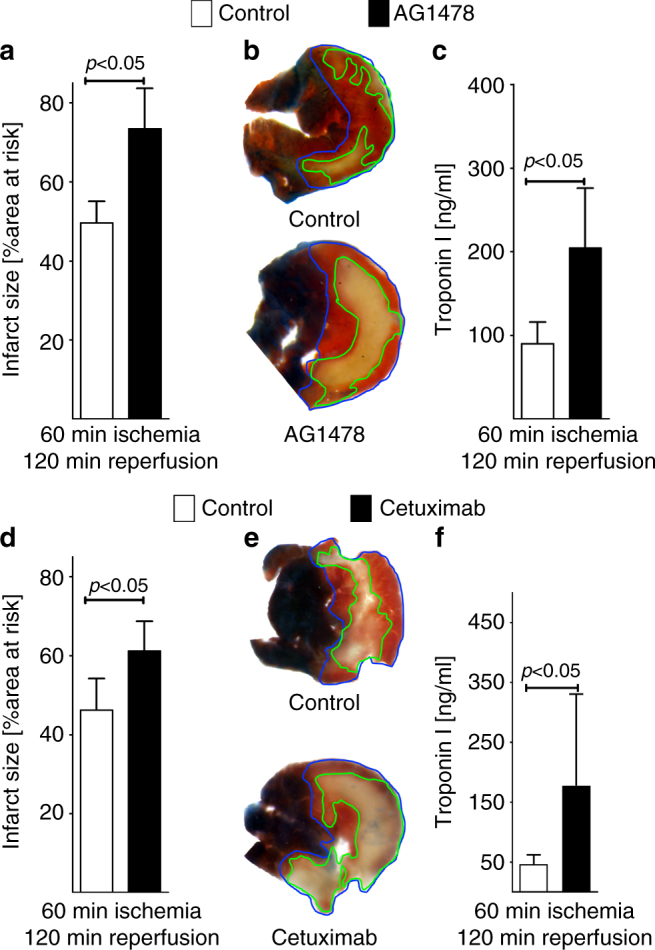
Pharmacologic inhibition of the amphiregulin receptor ErbB1 during murine myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. a–c Mice underwent 60 min of myocardial ischemia, followed by 120 min of reperfusion; infarct sizes were measured by double staining with Evan’s blue and triphenyltetrazolium chloride and serum samples were collected. All infarct sizes are presented as the percentage of infarcted tissue in relation to the area-at-risk. Serum Troponin levels were determined by ELISA. a Infarct sizes of C57/BL6 mice after 60 min of ischemia and 120 min reperfusion, treated prior to myocardial ischemia reperfusion with vehicle or an ERBB1-specific inhibitor (AG1478), administered 15 min prior to ischemia via an indwelling arterial catheter. Data presented as the percentage of infarcted area in relation to area-at-risk (n = 4 per group). b Representative infarct staining of C57/BL6 treated with vehicle or AG1478. c Troponin serum levels of C57/BL6 mice, after 60 min ischemia, 120 min reperfusion, treated with vehicle or AG1478 (n = 5 per group). d Infarct sizes of C57/BL6 mice after 60 min of ischemia and 120 min reperfusion, treated 15 min prior to ischemia via an indwelling arterial catheter with vehicle or a highly specific ERBB1-specific inhibitor (Cetuximab). Data presented as the percentage of infarcted area in relation to area-at-risk (control n = 4; cetuximab n = 8). e Representative infarct staining of C57/BL6 treated with vehicle or Cetuximab. f Troponin serum levels of C57/BL6 mice after 60 min ischemia, 120 min reperfusion, treated with vehicle or Cetuximab (n = 7 per group). All data in this figure is presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance assessed by two-sided, unpaired Student’s t-test
