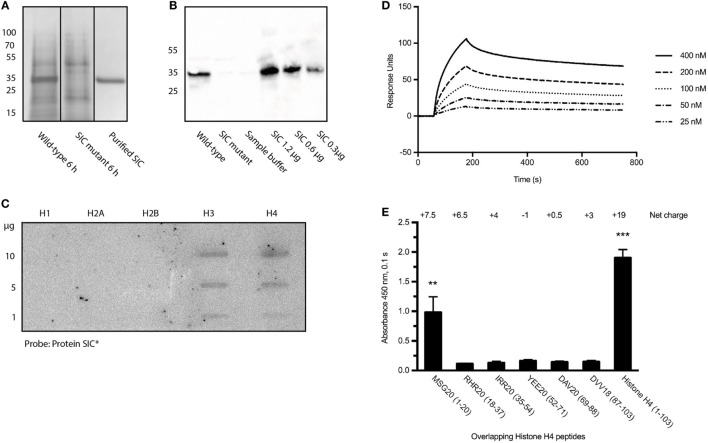
Figure 1.
Streptococcal inhibitor of complement (SIC) expression and its binding to histones. (A) S. pyogenes wild-type and SIC-mutant SNs were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid and separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE. (B) SIC was identified in SNs using rabbit antisera against SIC. (C) An Immobilon filter was immobilized with different histone subtypes, incubated with 125I-labeled SIC and bound probe was detected with the Fuji FLA-3000 imaging system. (D) SPR technology was used to show the interaction between histone H4 and SIC. Histone H4 was coated on a CM5 Sensor Chip and SIC was applied in a flow at different concentrations. (E) Microtiter plates were coated with histone H4-derived peptides and probed with SIC. Binding was detected using rabbit antisera against SIC and visualized by a peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. Data show means ± SEM (one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s test). All experiments were independently performed at least three times and one representative image is shown. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001.