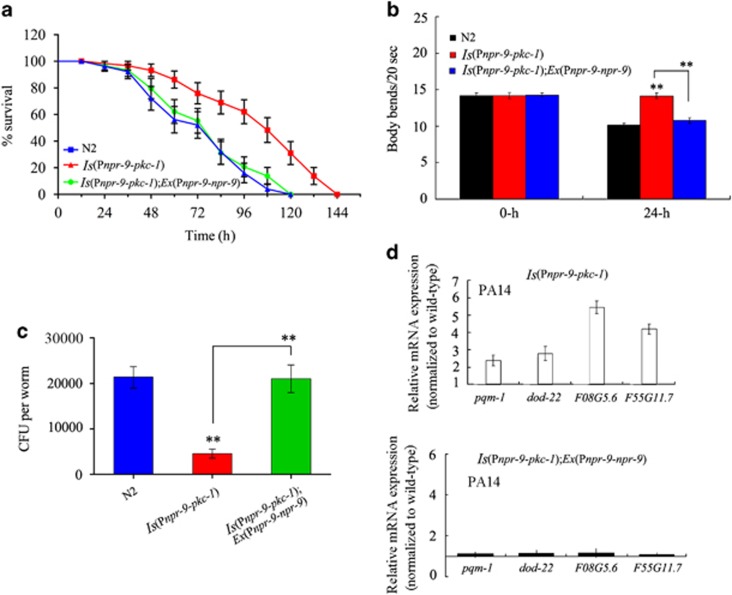
Figure 6.
NPR-9 inhibited the effects of a gain-of-function protein kinase C mutation, (pkc-1(gf)), on innate immunity in AIB interneurons. (a) Effects of npr-9 overexpression on the survival curve of nematodes exposed to P. aeruginosa PA14, expressing gain-of-function protein kinase C (pkc-1(gf)) mutations in their AIB interneurons. A statistical comparison of the survival plots indicates that survival of nematodes expressing gain-of-function, protein kinase C (pkc-1(gf)) mutations in AIB interneurons was significantly different from that of wild-type N2 animals (P<0.0001), whereas the survival plots indicate that the survival of Ex(Pnpr-9-pkc-1);Ex(Pnpr-9-npr-9) nematodes was not significantly different from that of wild-type N2 animals (P=0.945). (b) Effects of npr-9 overexpression on body bend in nematodes exposed to P. aeruginosa PA14 and expressing gain-of-function protein kinase C (pkc-1(gf)) mutations in their AIB interneurons. Bars represent the mean±s.d. **P<0.01 vs N2 (if not specially indicated). (c) Effects of npr-9 overexpression on CFU of nematodes expressing gain-of-function protein kinase C (pkc-1(gf)) mutations in AIB interneurons in animals exposed to P. aeruginosa PA14. Bars represent the mean±s.d. **P<0.01 vs N2 if not specially indicated. (d) Effects of npr-9 overexpression on the expression patterns of immunity-related genes in nematodes expressing gain-of-function protein kinase C (pkc-1(gf)) mutations in AIB interneurons and exposed to P. aeruginosa PA14. Normalized expression is presented relative to wild-type expression. Bars represent the mean±s.d. CFU, colony-forming unit.