Figure 2.
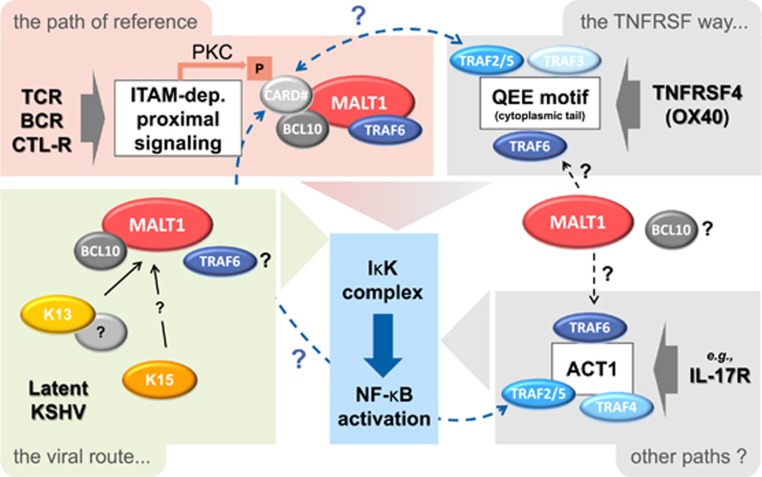
Toward novel ways of MALT1 activation?. ‘The path of reference’ represents the classical pathway of MALT1 activation as depicted in Figure 1. TCR, T-cell receptor; BCR, B-cell receptor; CTL-R, C-type lectin receptor. ‘The TNFRSF way…’ is based on an understanding of and questions about signaling and NF-κB activation in the context of the OX40 pathway. OX40 stimulation leads to the recruitment of TRAF proteins at the cytoplasmic tail of the receptor,10 which might enable recruitment of a CBM complex11 via binding of a CARD protein to TRAF2(ref. 12) or lead to recruitment of MALT1 by TRAF6, perhaps together with BCL10.2, 9 ‘Other paths?’ refers to pathways relying on signaling hubs able to recruit TRAF proteins, such as the IL-17R pathway via the protein, ACT1, which could potentially attract MALT1 in similar ways as proposed for the OX40 pathway. Finally, ‘the viral route’ summarizes the recent findings3 that two viral proteins, K13 and K15, from KSHV can activate MALT1 in a BCL10-dependent and likely CARD-independent manner—K13 binds to MALT1, possibly indirectly, whereas K15 does not—thus representing potential novel MALT1 activation pathways. CARD# represents CARD11 for antigen receptor (TCR/BCR) signaling; CARD9 for C-type-lectin (CTL)-receptor signaling and potentially stands for the four CARD/CARMA family proteins (CARD9, CARD10, CARD11, CARD14) or isoforms thereof, in case of the hypothesized signaling crosstalks depicted in the figure.