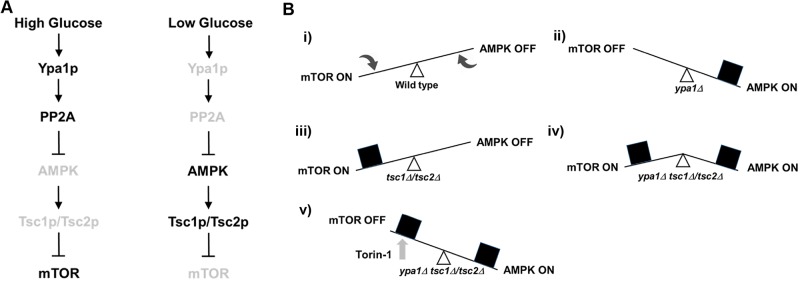
Fig. 7.
Model describing the putative role of Ypa1p in mTOR signaling in fission yeast. (A) Hypothesized signaling axis extending from the sensing of glucose levels via Ypa1p to the activation of mTOR. Components listed in black type are considered fully active. Components listed in grey type are considered minimally active. (B) Abstract model describing the effects of mutations in ypa1 and tsc1/tsc2, both singly and in combination. (i) In the presence of glucose mTOR activity is high and AMPK activity is low. However, the system is free to shift in either direction as a function of glucose concentration. (ii) In ypa1Δ mutants, AMPK is locked in the ON position. The cell is maladapted, but the metabolic signals being output are consistent. (iii) In tsc1Δ/tsc2Δ mutants mTOR is locked in the ON position. The cell is maladapted, but again the metabolic signals being output are consistent. (iv) In ypa1Δ tsc1Δ/tsc2Δ mutants both mTOR and AMPK are locked in the ON position. The metabolic signals being output are contradictory, resulting in a synthetic growth defect. (v) Torin-1 treatment rescues the growth defect by turning mTOR OFF and restoring the balance.