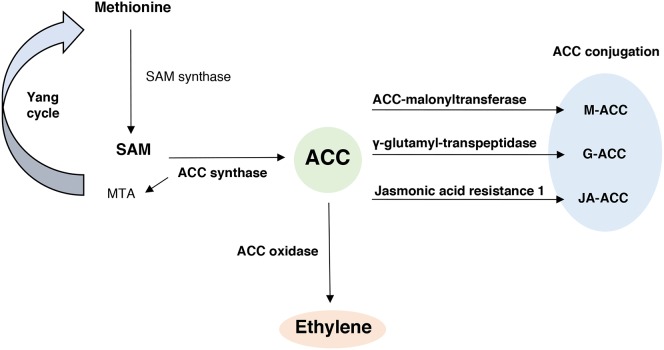
FIGURE 1.
The ethylene biosynthetic pathway and ACC conjugation process. In this pathway methionine is converted to S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) by the enzyme SAM synthase. SAM is converted to ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) and 5-methylthioadenosine (MTA), by the enzyme ACC synthase. MTA is reconverted to methionine by a series of biochemical reactions, described as the Yang cycle. The enzyme ACC oxidase catalyzes the conversion of ACC to ET. In addition, ACC can be conjugated to M-ACC (Malonyl-ACC), G-ACC (γ-glutamyl-ACC) or JA-ACC (Jasmonoyl-ACC) by the action of the enzymes ACC-malonyl transferase, γ-glutamyl-transpeptidase and Jasmonic acid resistance 1, respectively.