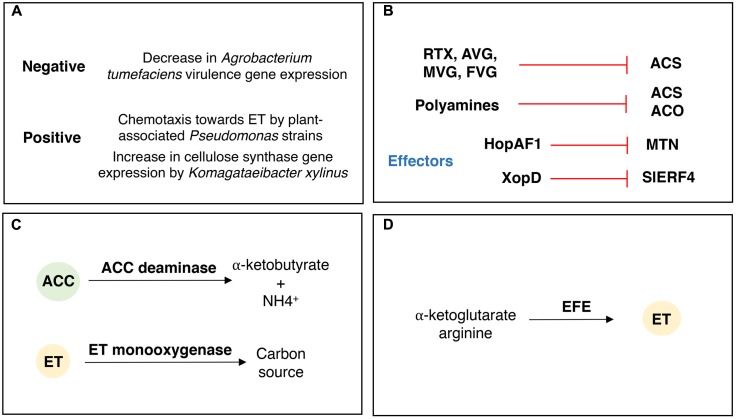
FIGURE 4.
Bacterial mechanisms involved in the responses to ethylene and modulation of plant ACC and ethylene levels. (A) Bacterial responses to ET, both positive and negative that relate to the ET effect in the expression of several genes and traits. (B) Compounds and effectors impacting plant ACC and ET biosynthesis and signaling. RTX, Rhizobitoxine; AVG, aminoethoxyvinylglycine; MVG, methoxyvinylglycine; FVG, 4-formylaminooxyvinylglycine; MTN, methylthioadenosine nucleosidase. (C) Bacterial degradation of plant ACC and ET. Bacteria presenting ACC deaminase activity catabolize ACC to produce α-ketobutyrate and ammonia. Bacteria producing an ET-monoxygenase and other associated components can use ET as sole carbon source. (D) Bacterial ET production. Some bacterial pathogens produce ET by the action of an ET-forming enzyme (EFE) that uses arginine and α-ketoglutarate as substrates.