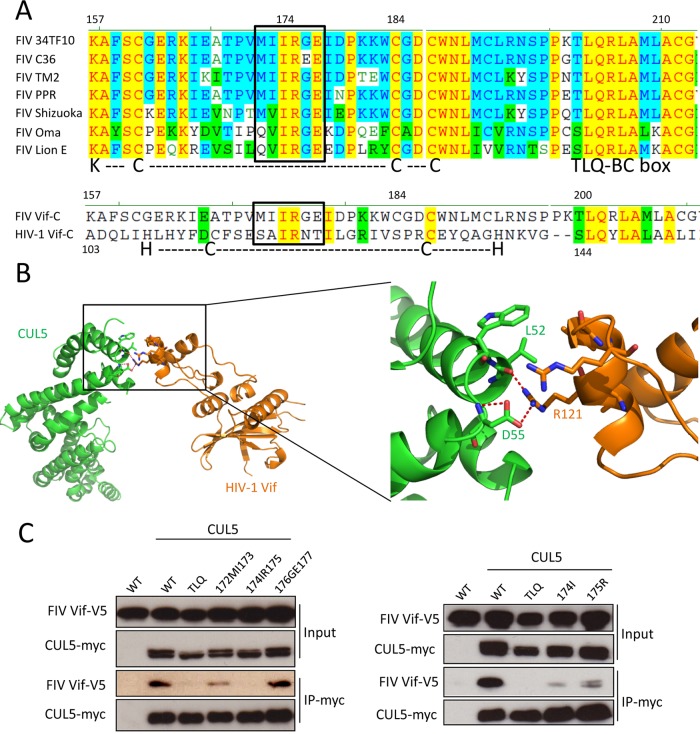
FIG 3.
Identification of determinants in the C terminus of FIV Vif that regulate binding to CUL5. (A, top) Sequence alignment of FIV Vifs from different FIV strains, including 34TF10, C36, TM2, PRR, Shizuoka, Oma (Pallas's cats), and lion subtype E. (Bottom) Sequence alignment of C-terminal residues of FIV Vif (clone 34TF10) and HIV-1 Vif (clone NL4-3). KCCC is a motif of FIV Vif that is similar to the HIV-1 Vif zinc interaction motif HCCH. The boxed region indicates a conserved hydrophobic motif. Nonsimilar residues are indicated in black with no background, conservative residues are indicated in blue with a cyan background, blocks of similar residues are indicated in black with a green background, identical residues are indicated in red with a yellow background, and weakly similar residues are indicated in green with no background. (B) Structure of the HIV-1 Vif-CUL5 complex (orange, Vif; green, CUL5) (PDB accession number 4N9F). A closeup view of the HIV-1 Vif-CUL5 interface is shown. The residues that are involved in the HIV-1 Vif-CUL5 interaction are indicated. Red dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds. (C) The FIV Vif 174IR175 region is important for the interaction of FIV Vif with CUL5. myc-CUL5 expression plasmids or the empty pcDNA3.1 plasmid was cotransfected with expression plasmids for wild-type FIV Vif-V5 or the indicated FIV Vif mutants. Immunoprecipitated complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-V5 for FIV Vif and with anti-myc for CUL5.