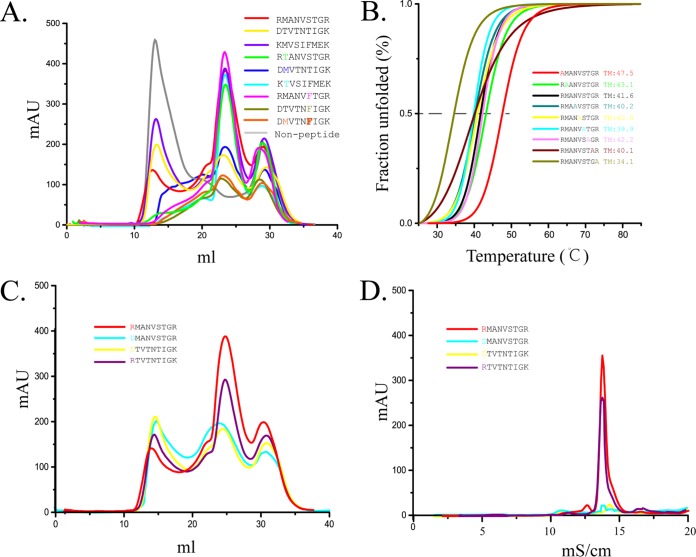
FIG 5.
Peptide binding with FLA-E*01801 indicated by in vitro refolding. Anchor residues of the FLA-E*01801 complex were tested by alanine scanning, CD spectroscopy, and peptide mutation. (A) FLA-E*01801 with three different wild-type peptides (RMA9, KMV9, and DTV9) and six mutant peptides (RMA9-P2T, KMV9-P2T, DTV9-P2M, RMA9-P6F, DTV9-P6F, and DTV9-P2MP6F) refolded in vitro and analyzed by chromatography on a Superdex 200 16/60 column. FLA-E*01801 without a peptide was included as a negative control. Peaks 1, 2, and 3 represent the heavy-chain polymer, the correctly refolded FLA-E*01801 complex, and the excess fβ2m, respectively. The relevant concentration ratios and altitudes of peak 2 formed by complexes with different peptides represent the refolding efficiencies. (B) Thermal stabilities of the FLA-E*01801 complex. The thermal stabilities of FLA-E*01801 with nine peptides (RMA9, RMA9-P1A, RMA9-P2A, RMA9-P4A, RMA9-P5A, RMA9-P6A, RMA9-P7A, RMA9-P8A, and RMA9-P9A) were tested by CD spectroscopy. (C) Gel filtration chromatograms of FLA-E*01801 complex with RMA9, RMA9-P1D, DTV9, and DTV9-P1R. (D) Anion-exchange chromatography of FLA-E*01801 complexes with RMA9, RMA9-P1D, DTV9, and DTV9-P1R. The complexes with RMA9 and DTV9-P1R were eluted at NaCl concentrations of 12% to 15%. The refolded complex proteins with RMA9-P1D and DTV9 disaggregated at NaCl concentrations of 12% to 15%, indicating instability.