FIG 1.
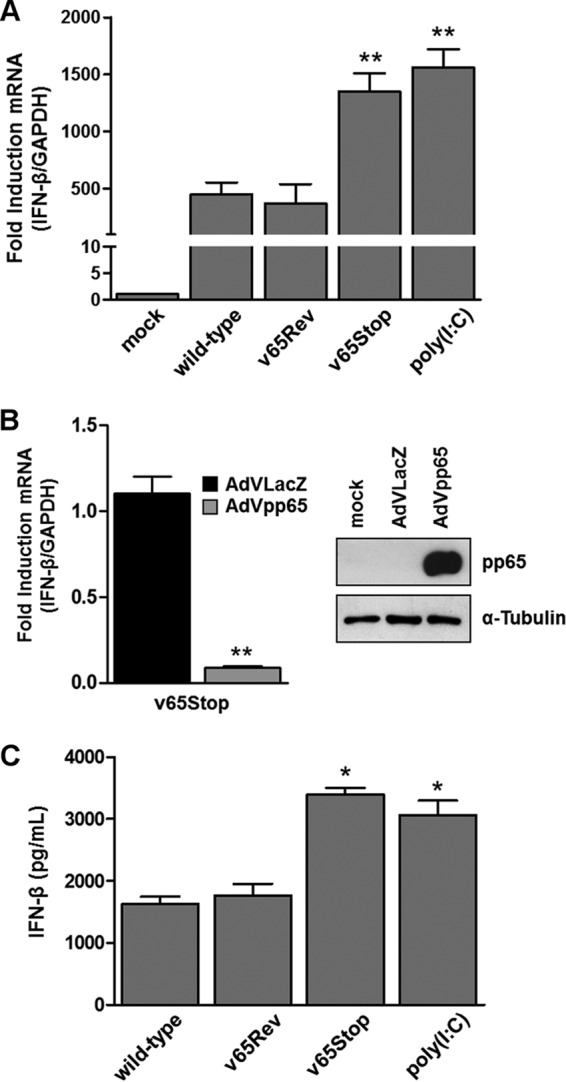
Inhibition of IFN-β response by HCMV pp65. (A) HFFs were infected at an MOI of 1 with wild-type, v65Rev, or v65Stop virus and processed by RT-qPCR. Kinetics analysis results for IFN-β mRNA expression following HCMV versus mock infection were normalized to those for GAPDH expression and are shown as mean fold changes plus SD (**, P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's posttest for comparison of treated versus untreated cells). (B) (Left) HFFs were transduced with AdVLacZ or AdVpp65 at an MOI of 50. Afterward, the cells were infected with v65Stop (MOI = 1). At 6 hpi, IFN-β mRNA expression was normalized to that of GAPDH and is shown as the mean fold change plus SD (**, P < 0.01; unpaired t test for comparison of AdVpp65- versus AdVLacZ-transduced cells). (Right) The efficiency of pp65 overexpression was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-pp65 monoclonal antibody; α-tubulin was included as a loading control. Experiments were repeated at least three times, and one representative result is shown. (C) HFFs were infected with the wild type, v65Rev, or v65Stop at an MOI of 1 or stimulated with poly(I·C) (4 μg/ml). Supernatants were collected at the indicated times postinfection and assessed by ELISA for IFN-β production. The results are shown as mean fold change plus SD [*, P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's posttest for comparison of wild-type/v65Rev- versus v65Stop/poly(I·C)-treated cells].
