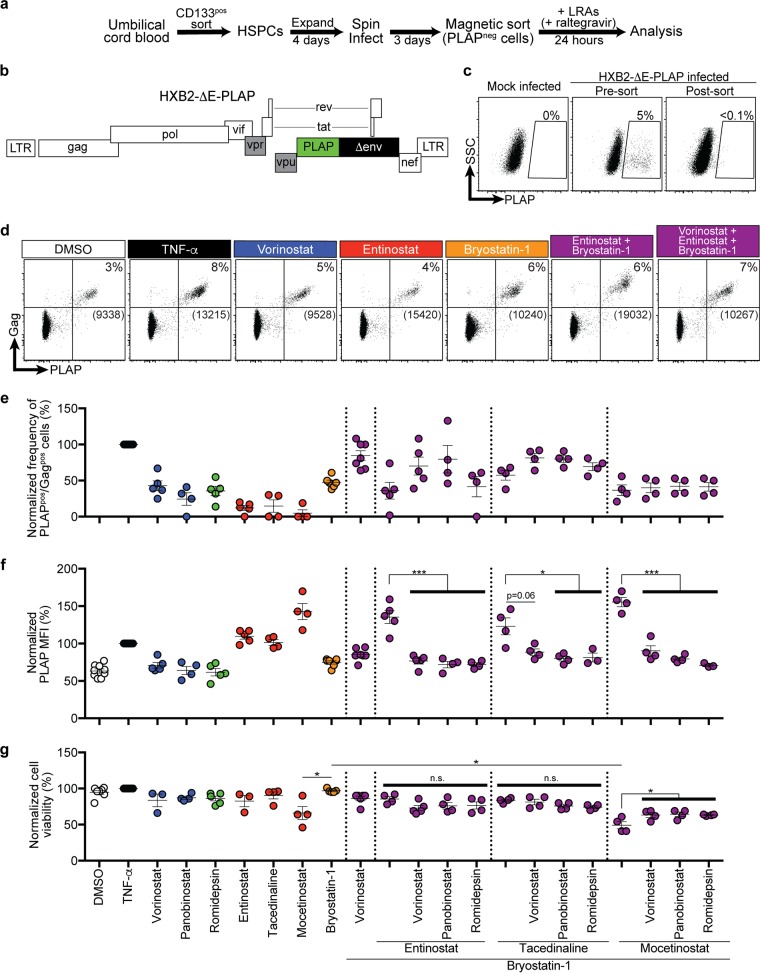
FIG 4.
Class 1-selective HDIs plus bryostatin-1 maximally induce latency reversal and viral protein production, whereas pan-HDIs are inhibitory when added to these combinations. (a) Schematic illustration of modified HIV latency model system in HSPCs. (b) Schematic diagram of the HXB2-based HIV molecular clone. Filled black and green rectangles indicate genes that have been deleted from or added to the wild-type molecular clone, respectively. Filled gray rectangles indicate genes that are dysfunctional in the wild-type HXB2 molecular clone. (c) Flow-cytometric analysis of mock-infected and sorted, infected HSPCs. Numbers above gates indicate the frequency of live PLAPpos cells. Live cells were gated based on FSC and SSC parameters. (d) Representative flow-cytometric analysis of infected HSPCs treated for 24 h with the indicated LRAs. Live cells were gated based on FSC and SSC. Numbers above gates indicate the frequencies of PLAPpos, Gagpos cells. Numbers in brackets indicate PLAP MFI of cells within the double-positive gate. Gates are based on mock-infected cells and staining with an isotype control antibody. Summary graphs of frequency of PLAPpos, Gagpos cells (e) and PLAP MFI of PLAPpos, Gagpos cells (f) and relative cell viability following treatment with the indicated LRAs (g). The frequency of spontaneous reactivation observed under DMSO solvent conditions was subtracted from each experiment to reflect the actual frequency of reactivated provirus. Data are presented as a percentage of the effect of TNF-α (mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3). P values were calculated by two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.