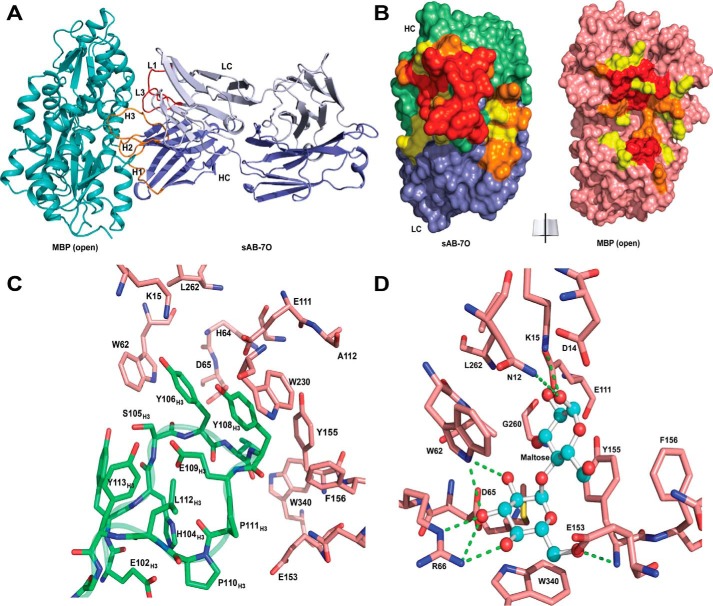
Figure 3.
Structures of open-specific sAB-7O·MBP complex. A, sAB-7O binds to MBP in open conformation by the light chain CDRs (L1 and L3) and heavy chain CDRs (H1, H2, and H3). B, open-book view of the interface between sAB-7O and MBP. Residues in the interface are colored according to their percentage of reduction in accessible surface area upon complex formation (yellow, 10–49%; orange, 50–70%; red, >70%). C, CDR-H3 residues of sAB-7O (green) interact with the residues in the maltose-binding pocket of MBP (salmon). D, residues of MBP (salmon) involved in maltose binding. Selected hydrogen-bonding interactions with maltose (ball and stick) are highlighted. Most of the maltose-binding residues in MBP are involved in interaction with CDR-H3 residues of sAB-7O as seen in C. Sugar rings and hydroxyl groups of maltose are mimicked by the aromatic ring of tyrosine and backbone carbonyls in CDR-H3 residues, resulting in strong bias of the maltose binding pocket as the sole immunodominant epitope.