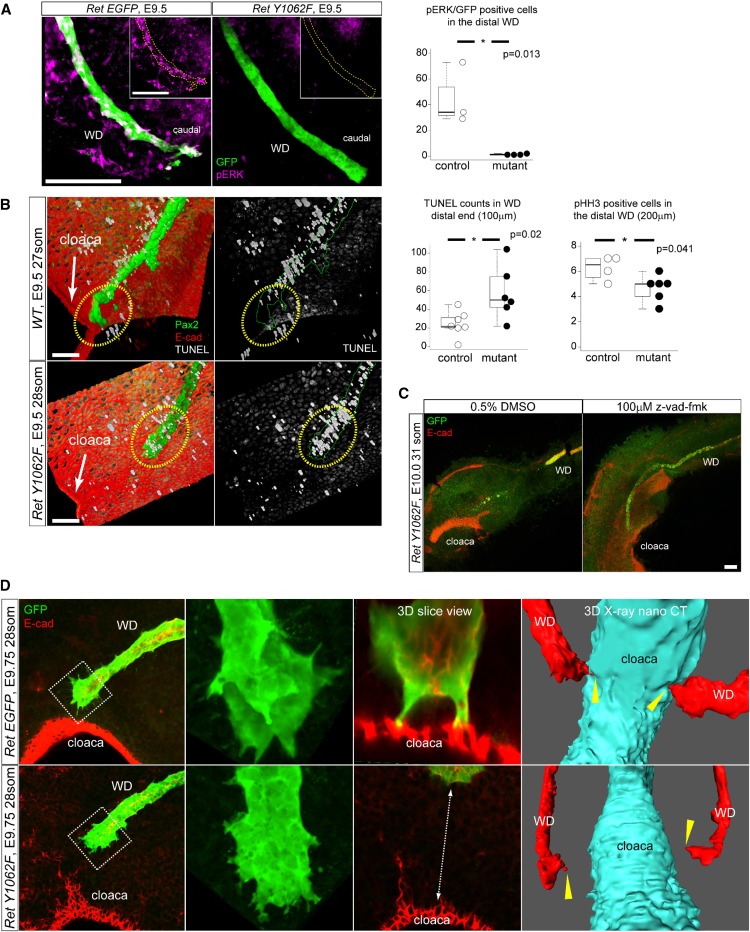
Figure 2.
Loss of ERK activity in RetY1062F WD tip causes increased apoptosis and migration defects to reach cloaca. (A) Whole-mount three-dimensional confocal immunofluorescence images with GFP (Ret-positive WD cells) and pERK antibodies reveal that the distal end of RetY1062F WDs shows lack of ERK activity at embryonic day 9.5. Yellow dotted lines outline the WD in the insets. Quantification of pERK/EGFP double-positive cells in the distal region (200 μm from the tip) of the WD shows significant reduction in RetY1062F mutant WD (control: 45.3±19.7, two litters, n=3; mutant: 1.3±0.4, three litters, n=4; P=0.01; mean±SD, t-test). (B) Three-dimensional reconstructed confocal z-stacked images of whole-mount immunofluorescence for TUNEL (white), Pax2 (green, WD), and E-cad (red, cloaca and body wall) in control (RetEGFP/+or WT) and RetY1062F (RetY1062F/EGFP) WDs. Note marked cell death in the distal end of WD in RetY1062F embryos at embryonic day 9.5. Control WD reaches cloaca and shows almost no TUNEL in the WD tip (top). Mutant WD tip shows extensive cell death preventing elongation and contact with cloaca (bottom). Yellow dashed circles represent WD tip region. Cell apoptosis measured by TUNEL staining in the distal region (100 μm from the tip) of WD is significantly increased in RetY1062F mutant (control: 24.6±12.3, two litters, n=6; mutant: 57.2±26.1, three litters, n=6; P=0.02; mean±SD, t-test). Cell proliferation measured by pHH3 immunofluorescence in the distal region (200 μm from the tip) of WD is significantly reduced in RetY1062F mice (control: 6.3±1.0, one litter, n=4; mutant: 4.7±1.0, one litter, n=6; P=0.04; mean±SD, t-test). (C) Inhibition of apoptosis in RetY1062F mutant WD at embryonic day 10.0 rescues defective elongation of WD toward cloaca. RetY1062F WDs treated with vehicle (DMSO) stop growing and fail to reach cloaca as observed in vivo (compare with Figure 1B). Growth defects of RetY1062F WD are rescued with z-vad-fmk treatment. Note that the 24-hour ex vivo culture is technically limited to assess if WD elongation is completely rescued, especially in WDs that are more severely affected. Images were acquired by confocal imaging with z-stacks of whole-mount immunofluorescence of cultured specimens with GFP (green, WD) and E-cad (red, WD and cloaca) antibodies. (D) RetEGFP WDs at embryonic day 9.5 show extensive sharp cellular protrusions in the advancing front as visualized by GFP (green, WD) and E-cad (red, cloaca) whole-mount three-dimensional confocal immunofluorescence microscopy maximal projection images. RetY1062F WDs lack terminal cellular protrusions and fail to reach cloacal epithelia (see also Supplemental Figure 5A, Supplemental Movies 2 and 3). Images on the right from embryonic day 9.75 whole three-dimensional x-ray nano-computed technology scanning further show WD-cloaca fusion and cellular protrusions defects in RetY1062F WDs (red, WD; cyan, cloaca). Yellow arrow heads represent the tip of the WD, which touched down on the cloaca in RetEGFP control embryo, whereas failed in RetY1062F mutant (see also Supplemental Figure 5B, Supplemental Movies 4 and 5). Scale bar, 100 μm. * denotes statistical significance.