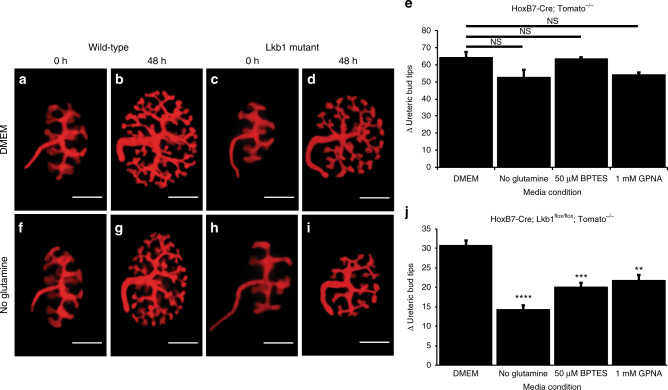
Fig. 2.
Perturbation of glutamine metabolism causes growth defect in embryonic Lkb1 mutant collecting ducts. Live images of E12.5 HoxB7-Cre; RosaTomato (n = 10) (a, b, f, g) and HoxB7-Cre; Lkb1flox/flox; RosaTomato (n = 10) (c, d, h, i) kidneys after 0 (a, f, c, h) or 48 (b, g, d, i) hours of culture in control media (DMEM, a−d) or DMEM lacking glutamine (f–i). Quantification of the change (Δ) in branch number (number of ureteric bud tips after 48 h—ureteric bud tips at 0 h) for HoxB7-Cre; RosaTomato (e) or HoxB7-Cre; Lkb1flox/flox; RosaTomato (j) kidneys grown in complete DMEM, DMEM-glutamine, DMEM+ 50 µM concentration of the glutaminase inhibitor BPTES, or 1 mM concentration of the Slc1a5 glutamine transporter inhibitor GPNA. n = 10 for each genotype under each condition. Statistical analysis via Mann−Whitney U-test **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, NS not significant. Error bars shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Scale bars equal 30 microns