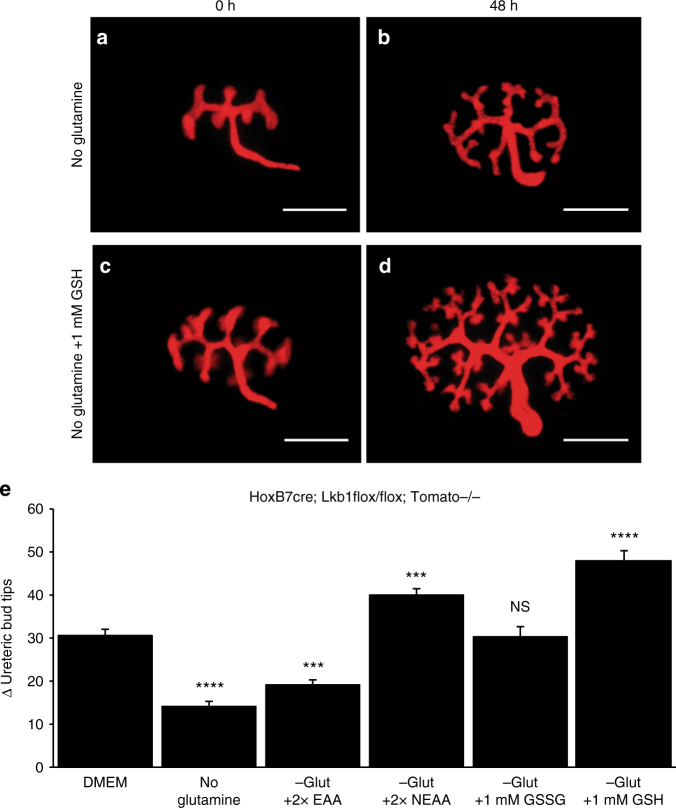
Fig. 4.
Exogenous sources of amino acids or glutathione rescues growth defect of Lkb1 mutant cells in the absence of glutamine. Live images of e12.5 HoxB7-Cre; Lkb1flox/flox; RosaTomato kidneys after 0 (a, c) or 48 (b, d) hours of culture in glutamine-deficient media (a, b) or glutamine-deficient media supplemented with 1 mm GSH (c, d). e Quantification of the change (Δ) in branch number (number of ureteric bud tips after 48 h—ureteric bud tips at 0 h) for e12.5 HoxB7-Cre;Lkb1flox/flox; RosaTomato kidneys grown in DMEM, DMEM-glutamine, DMEM-glutamine + 2× essential amino acids, DMEM-glutamine + 2× non-essential amino acids, DMEM-glutamine + 1 mm oxidized glutathione (GSSG), or DMEM-glutamine + 1 mm reduced glutathione (GSH). Note that supplementation with NEAAs, GSSG, or GSH is capable of restoration of Lkb1 mutant collecting duct branching equal to or above levels seen in control media. All statistical comparisons are relative to DMEM conditions. n = 10 for each condition. Statistical analysis via Mann−Whitney U-test, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, NS not significant. Error bars shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Scale bars equal 30 microns