Figure 1.
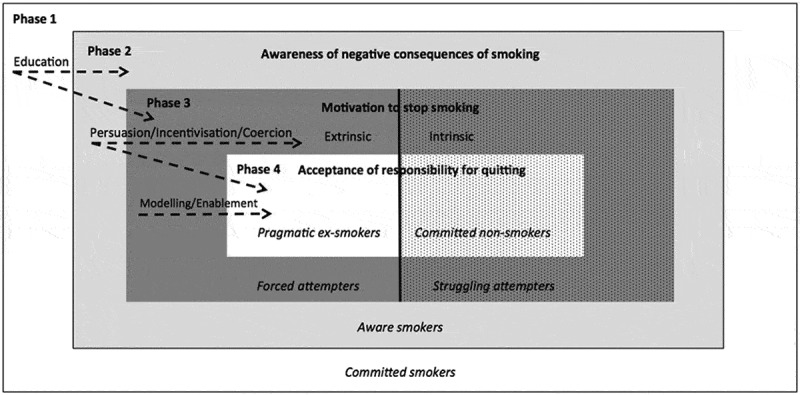
A parsimonious model of the progression towards smoking cessation with potential intervention functions that could influence behavior change. Phases of progression towards cessation are in bold. Typologies are in italics. Solid line represents locus of motivation to stop smoking (solid background = extrinsic; dotted background = intrinsic). Dashed arrows represent intervention functions from the Behavior Change Wheel (BCW)(Michie et al., 2014b) that could influence progression towards smoking cessation. In this model, people may jump phases (e.g. from phase 1 of not attempting to quit smoking to phase 4 of quitting successfully) or move back and forth between phases (e.g. between phases 4 and 3 stopping smoking and then relapsing) being influenced by intrapersonal and environmental factors (e.g., nicotine dependence, availability of support).
