Table 1. . The miRNAs carried by tumor-derived exosomes and delivered to immune cells induce protumorigenic functions.
| miRNA carried by TEX | Tumor type | Recipient cell | Acquired functions | Consequences for recipient cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 miR-29a | NSLC | TAMs |
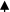 NF-κB pathway NF-κB pathway |
|
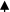 IL-6, IL-6, 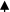 TNF-α TNF-α |
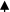 Proinflammatory phenotype Proinflammatory phenotype |
|||
| miR-203 miR-212p |
PAC | DCs |
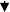 TLR-4 TLR-4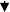 TNF-α, TNF-α, 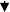 IL-12 IL-12 |
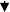 DC maturation DC maturation DC dysfunction DC dysfunction |
| miR-214 | Various human or mouse tumors | T cells |
 Treg Treg PTEN PTEN IL-10 IL-10 |
 Immune
suppression Immune
suppression |
| miR-183 | Human tumor cell lines | NK cells |
 TGF-β TGF-β DAP12 DAP12 |
 Lytic functions Lytic functions |
| miR-92a | Glioma | NKT cells |
 Perforin Perforin FasL FasL IFN-γ IFN-γ CD8+ T cells CD8+ T cells |
 Tumor apoptosis Tumor apoptosis Antitumor activity Antitumor activity |
Selected examples of miRNA interactions with different types of immune cells are presented. For a detailed review of TEX-associated miRNAs and their biological effects, see [34].
DC: Dendritic cell; NK: Natural killer; NSLC: Non-small-cell lung cancer; PAC: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage; TEX: Tumor-derived exosome.
