Figure 6. Gene expression and correlation of AMPA receptor subunits in the RVLM.
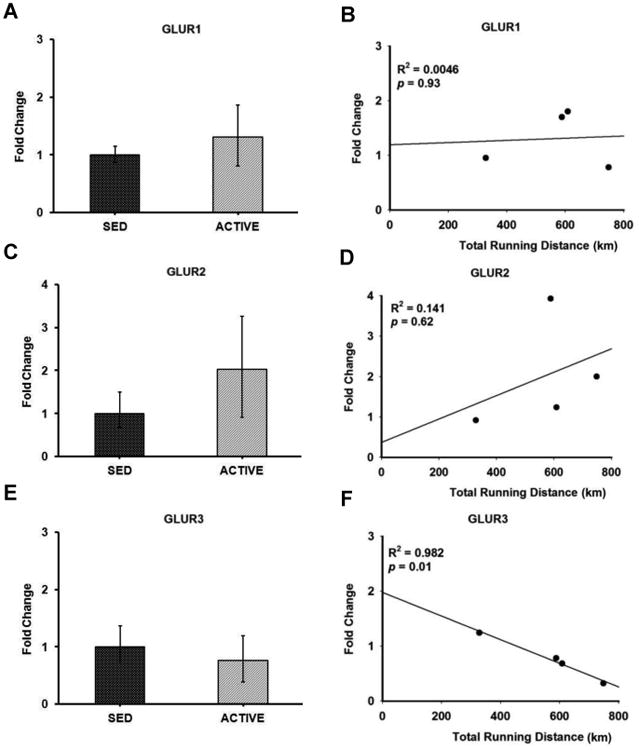
Bar graphs compare the gene expression of AMPA receptor subunits GLUR1 (A), GLUR2 (C) and GLUR3 (E) in spinally-projecting RVLM neurons between sedentary and active rats measured by real-time qRT-PCR. Data presented as fold change ± S.D. Correlation was determined between the total running distance in active animals and fold change of AMPA receptor subunits GLUR1 (B), GLUR2 (D) and GLUR3 (F) in spinally-projecting RVLM neurons. Gene expression of GLUR3 showed inverse correlation with the total running distance (p = 0.01) suggesting that physical activity could contribute to GLUR3 neuroplasticity in the RVLM.
