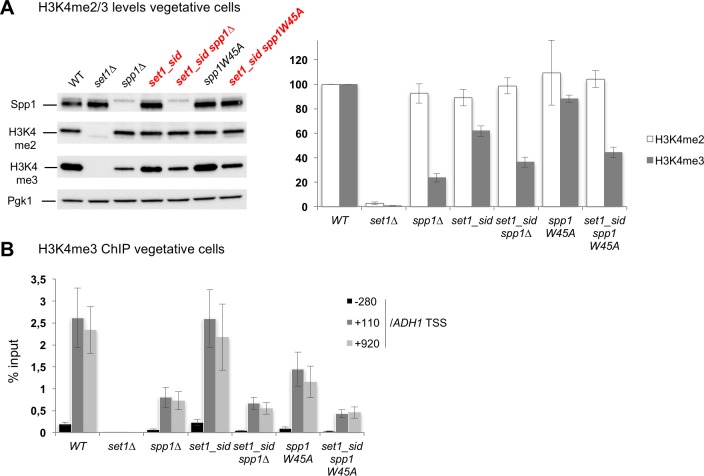
Fig 5. In the set1_sid mutant, Spp1 is still important to maintain H3K4me3 levels.
(A) Histone H3K4 methylation levels in vegetatively growing cells detected by Western blot. Anti-Spp1, anti H3K4me2, anti-H3K4me3 or anti-Pgk1 antibodies were used, as indicated. A representative experiment is shown. WT: ORT4601; set1∆: ORT4784; spp1∆: VBH152; set1_sid: VBH1881; set1_sid spp1∆: VBH1972; spp1W45A: VBH1419; set1_sid spp1W45A: VBH2021. The bar graph on the right indicates histone modification levels normalized to Pgk1 levels and relative to the WT strain. Values are the mean ± S.E.M. of the normalized relative levels from 3 to 6 replicates for each strain, except for spp1W45A, where only 2 replicates are available and the error bars indicate the range. See also S4 Table. (B) Histone H3K4me3 levels in vegetatively growing cells detected by ChIP at the highly transcribed ADH1 gene. Same strains as in A. Values are expressed as % of input DNA, and are the mean ± S.E.M. of six independent experiments.