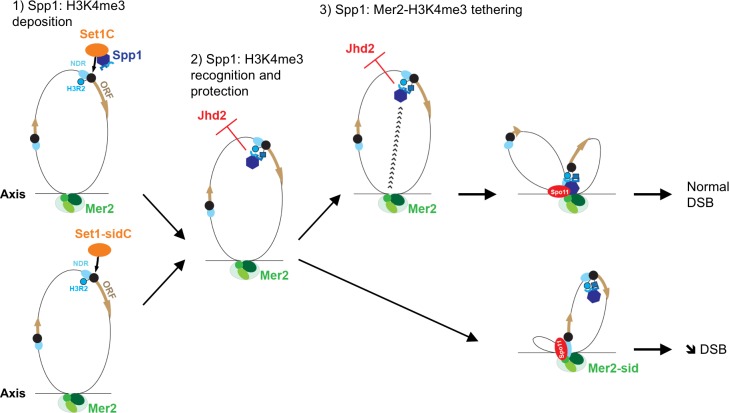
Fig 7. Illustration of the different functions of Spp1 for H3K4me3 and meiotic DSB formation.
1) in the Set1 complex, Spp1 has a role to allow catalysis of H3K4 trimethylation by Set1, but this function is not essential, since the set1-sid mutant still maintains high levels of H3K4me3. 2) In addition, Spp1 maintains H3K4me3 levels, not by stimulating Set1 catalytic activity, but likely by binding H3K4me3 with its PHD finger. This can take place without interaction with the Set1 complex. We propose this may protect H3K4me3 from active demethylation, by the Jhd2 enzyme. Other possible explanations are described in the text. 3) Finally, the simultaneous binding of Spp1 to H3K4me3 and to the axis-associated Mer2 protein is essential to promote efficient DSB formation by Spo11. It has to be noted that a PHD finger mutant of Spp1 (W45A) is still able to bind Mer2 [18], so recognition of H3K4me3 by Spp1 PHD finger is not a prerequisite for its subsequent binding to Mer2. NDR: nucleosome-depleted region; Black circle: first nucleosome of genes; H3R2: arginine 2 of histone H3, in its non-asymmetrically methylated form. The blue square represents H3K4me3.