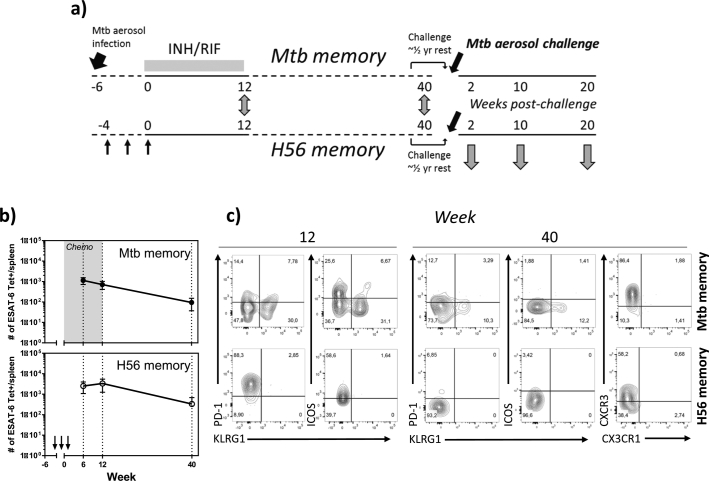
Fig. 1.
Resting memory cells after a cleared Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection show a higher degree of differentiation than memory cells primed by H56/CAF01 vaccination.
A) Schematic overview of the experimental outline. C57BL/6 mice, aerosol infected for 6 weeks, were subjected to a 12 week Isoniacid/Rifabutin (INH/RIF) treatment. ESAT-6 specific memory cells in the spleen were phenotypically characterized at week 12/End of Treatment (EoT) by ESAT-64-17:I-Ab pulldown using magnetic bead-based tetramer enrichment and compared to E6 memory responses 12 week post three s.c. immunizations with H56/CAF01, each spaced by two weeks. ESAT-6 specific memory cells in the spleen were similarly characterized and compared between the two groups of resting memory mice at week 40 after immunization/start of treatment. In order to study protective efficacy, H56 and Mtb memory mice were allowed to rest for half a year and then aerosol infected with Mtb Erdman. Protective efficacy was evaluated at week 2, 10 and 20 after challenge. B) The number of ESAT-64-17-specific CD4 T cells in the spleen was determined by Tetramer pulldown in Mtb (upper panel) and H56 (lower panel) memory mice at week 6, 12 and 40. Symbols, mean ± s.d. of 3–4 mice per time point. For Mtb memory mice, the experiment was repeated twice at week 6 and once at week 12 and 40. For H56 mice, the experiment was repeated twice at week 6 and 12 and once for week 40. C) Representative flow cytometry plots depicting KLRG1, PD-1, ICOS and CXCR3 (wk 40) expression by ESAT-6 tetramer-binding CD4 T cells in the spleen of Mtb (upper panels) and H56 (lower panels) memory mice at week 12 and 40.