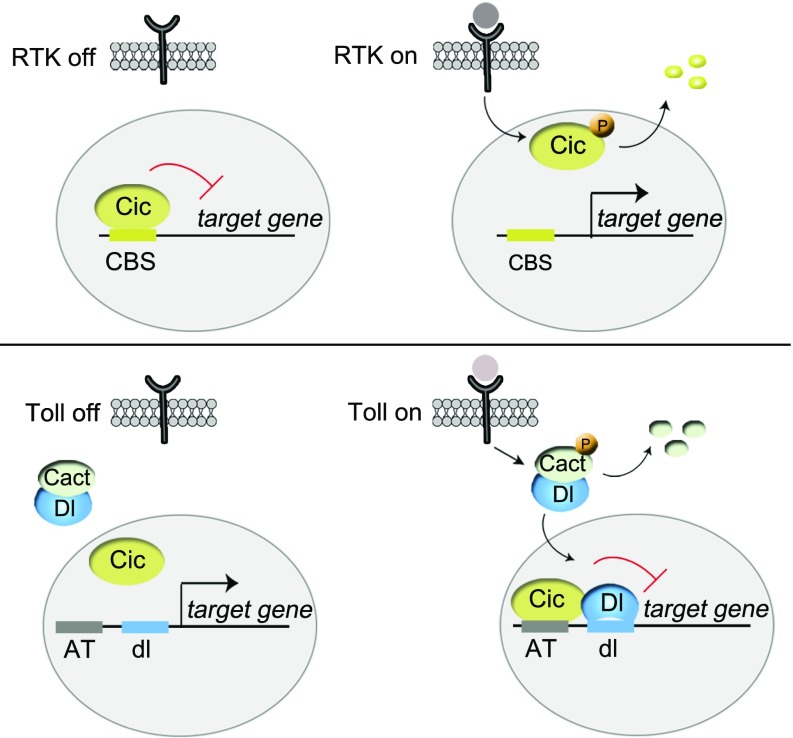
Fig. 6.
Different modes of Cic regulation in RTK- and Toll-dependent transcriptional control. (Upper) As a default repressor of RTK target genes, Cic binds to optimal CBSs in those genes and represses them in the absence of signaling. Following RTK activation, Cic is down-regulated via MAPK-mediated phosphorylation (P), which leads to derepression of its targets. (Lower) In contrast, in the context of Toll signaling, Cic functions via suboptimal AT sites that are not recognized by Cic when the signal is off. Upon Toll activation, Dorsal (Dl/dl) translocates into the nucleus and facilitates Cic binding to the AT sites.