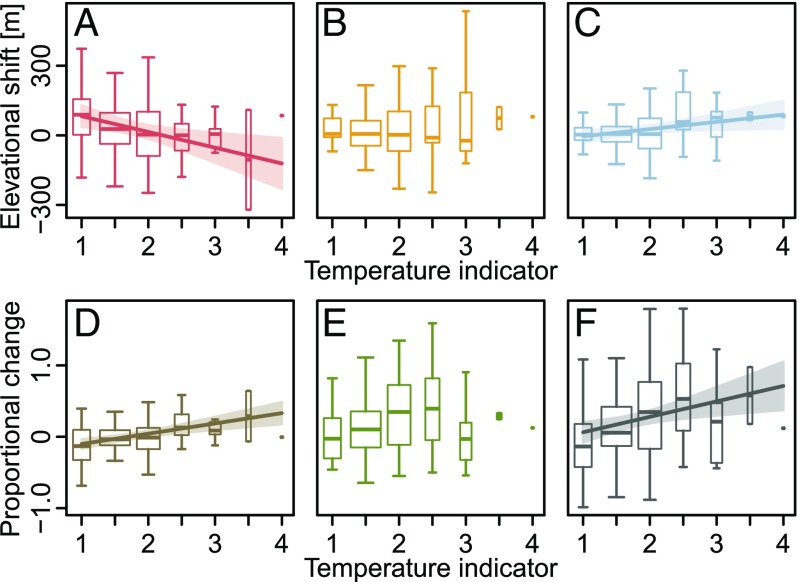
Fig. 4.
Relationships between changes of range attributes and temperature indicator values for 178 mountain plant species of the European Alps. (A) Rear edges, (B) optima, (C) leading edges, (D) elevational range size, (E) abundance, and (F) sum of proportional elevational range size and abundance changes. Lines and their shades represent significant linear regression models (Table S2) with their confidence intervals. The width of the boxplots is proportional to the number of species with the respective indicator value. Outliers have been removed to improve clarity. Indicator values were taken from Landolt et al. (26): 1, alpine to nival; 1.5, lower alpine to upper subalpine; 2, subalpine; 2.5, lower subalpine to upper montane; 3, montane; 3.5, lower montane to upper colline; and 4, colline.