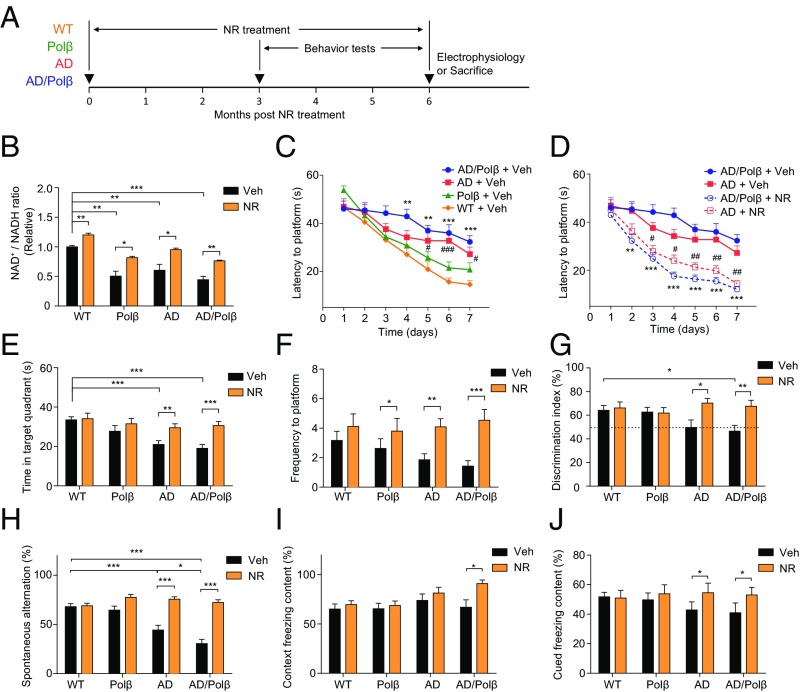
Fig. 1.
NR improves learning and memory in AD/Polβ mice. (A) Experimental design for NR treatment in WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice. (B) Effects of NR supplementation on the NAD+/NADH ratio in cortex tissue of WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice. (C and D) Effects of NR supplementation on the learning of vehicle- or NR-treated WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice measured by Morris water maze test. For C, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, AD/Polβ versus WT; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001, AD versus WT. For D, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NR versus vehicle in AD/Polβ; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, NR versus vehicle in AD; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. (E and F) Time in target quadrant (E) and frequency of platform location (F) in the probe trial of the Morris water maze test in WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice. (G) Effects of NR in object-recognition test in WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice with two different objects. (H) Effects of NR on the SAP changes in the Y-maze test in WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice. For B–H, n = 17 (WT + Veh), 16 (Polβ + Veh), 16 (AD + Veh), 16 (AD/Polβ + Veh), 13 (WT + NR), 12 (Polβ + NR), 14 (AD + NR), and 15 (AD/Polβ + NR) mice. (I and J) Effects of NR on fear memory in the context (I) or cued (J) fear conditioning test in WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice. n = 15 (WT + Veh), 15 (Polβ + Veh), 10 (AD + Veh), 9 (AD/Polβ + Veh), 13 (WT + NR), 12 (Polβ + NR), 10 (AD + NR), and 9 (AD/Polβ + NR) mice. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.