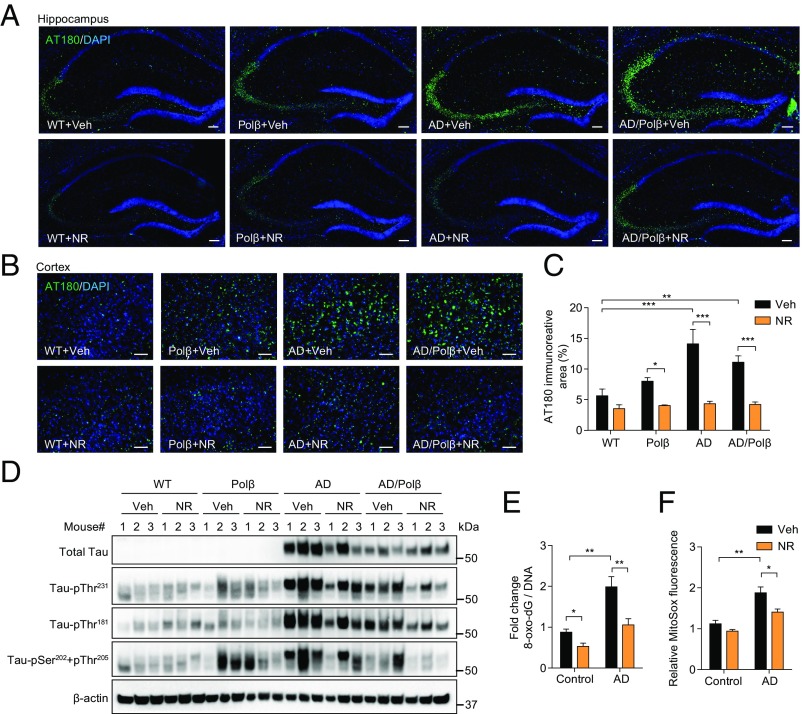
Fig. 4.
NR decreases tau phosphorylation in AD/Polβ mice and decreases oxidative damage in human AD fibroblasts. (A and B) Representative images of AT180 (green) and DAPI (blue) staining of hippocampus regions (A) and cortex regions (B) from WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice treated with vehicle or NR. (Scale bars, 100 µm.) (C) Quantification of the AT180+ immunoreactive area from sections as in B. n = 5 mice per group. (D) Representative immunoblots of the indicated Tau or pTau proteins from the hippocampus of WT, Polβ, AD, and AD/Polβ mice after treatment with vehicle or NR. Quantification of data is shown in Fig. S5. (E) ELISA of 8-oxo-dG in AD human fibroblasts and control fibroblasts with or without NR treatment (1 mM for 24 h). (F) Mitochondrial superoxide production measured by MitoSOX in AD human fibroblasts and control fibroblasts with or without NR treatment (1 mM for 24 h). For C, E, and F, data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.