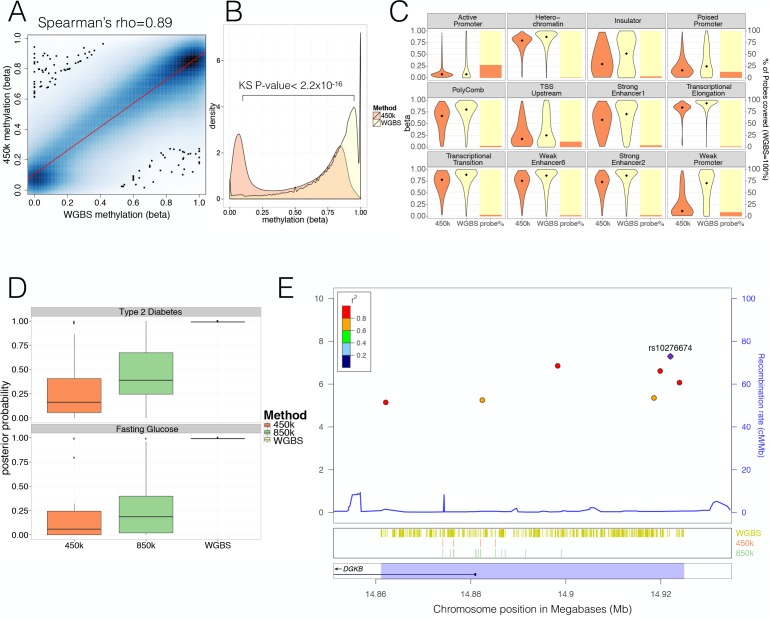
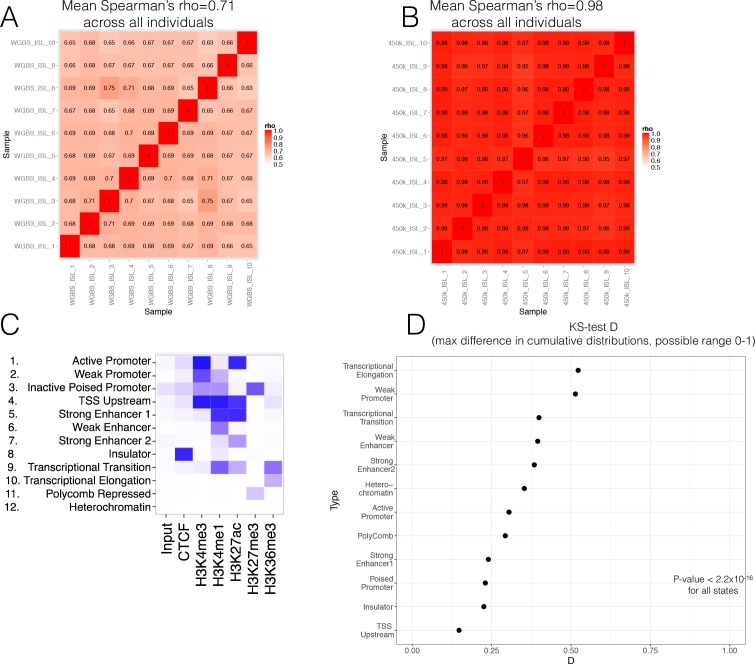
Figure 1. Comparison of human pancreatic islet WGBS and 450 k methylation data across the genome.
(A) Smooth Scatter plot shows Spearman’s rho correlation between the 450 k array (y-axis) and WGBS (x-axis) at overlapping sites. Darker colour indicates higher density of sites. (B) Comparison of the 450 k array (orange) and WGBS (yellow) methylation levels (x-axis) of all CpGs genome-wide assayed by either method (y-axis shows density). The P-value shown is derived using a Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test. (C) For each chromatin state from Parker et al. (2013) the methylation levels of all CpG sites independent of overlap (diamond indicates the median) are shown as violin plots (left y-axis) and the CpG probe percentage per state for the 450 k array (orange) and WGBS (yellow) are shown as bar-plot (right y-axis). The 450 k probes represent the percentage of the total number of CpG sites which is determined by the number of WGBS CpG sites detected (WGBS = 100%). (D) Distribution of GWAS Posterior Probabilities (Type 2 Diabetes and Fasting Glucose) captured by CpG sites on the 450 k array (orange), 850 k array (green) and WGBS (yellow/black line). (E) Locuszoom plot showing CpG density and credible set SNPs. SNPs are shown with P-values (dots, y-axis left), recombination rate (line, y-axis right) and chromosome positions (x-axis) while CpG and gene annotations are shown below. These annotations include CpGs identified from WGBS (yellow stripes), 450 k CpG probes (orange stripes), 850 k CpG probes (green stripes) and gene overlap (DGKB label). The highlighted region in blue captures the 99% credible set region plus additional 1000 bp on either side. At the very bottom the position on chromosome seven is shown in Megabases (Mb).